Downloads: Windows: x64 Arm64 | Mac: Universal Intel silicon | Linux: deb rpm tarball Arm snap
Welcome to the October 2023 release of Visual Studio Code. There are many updates in this version that we hope you’ll like, some of the key highlights include:
If you’d like to read these release notes online, go to Updates on code.visualstudio.com.
Insiders: Want to try new features as soon as possible? You can download the nightly Insiders build and try the latest updates as soon as they are available.
Accessibility
Contents
- 1 Accessibility
- 2 Workbench
- 3 Editor
- 4 Source Control
- 5 Notebooks
- 6 Debug
- 7 Remote Development
- 8 Contributions to extensions
- 8.1 GitHub Copilot
- 8.1.1 Streaming inline chat
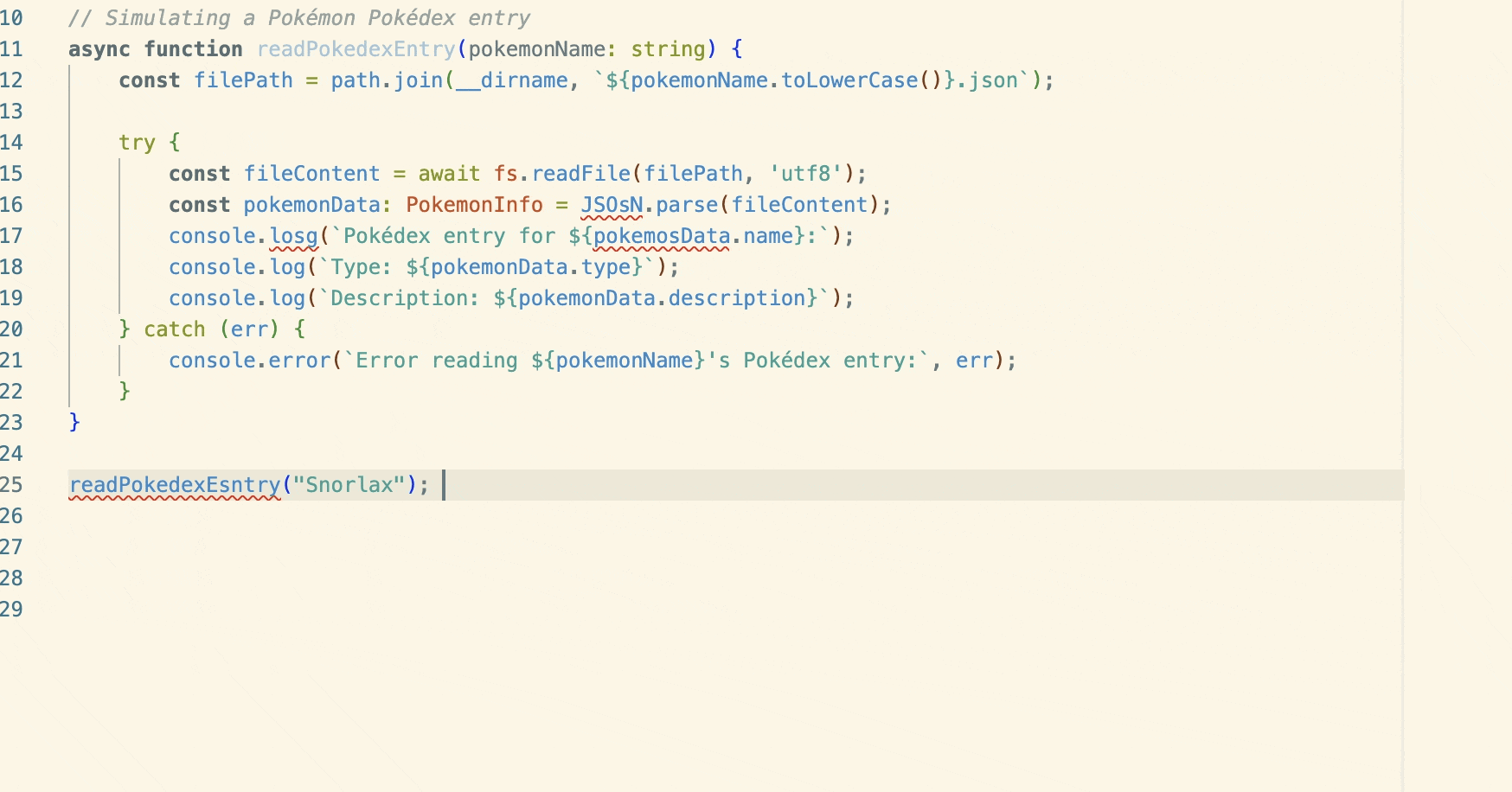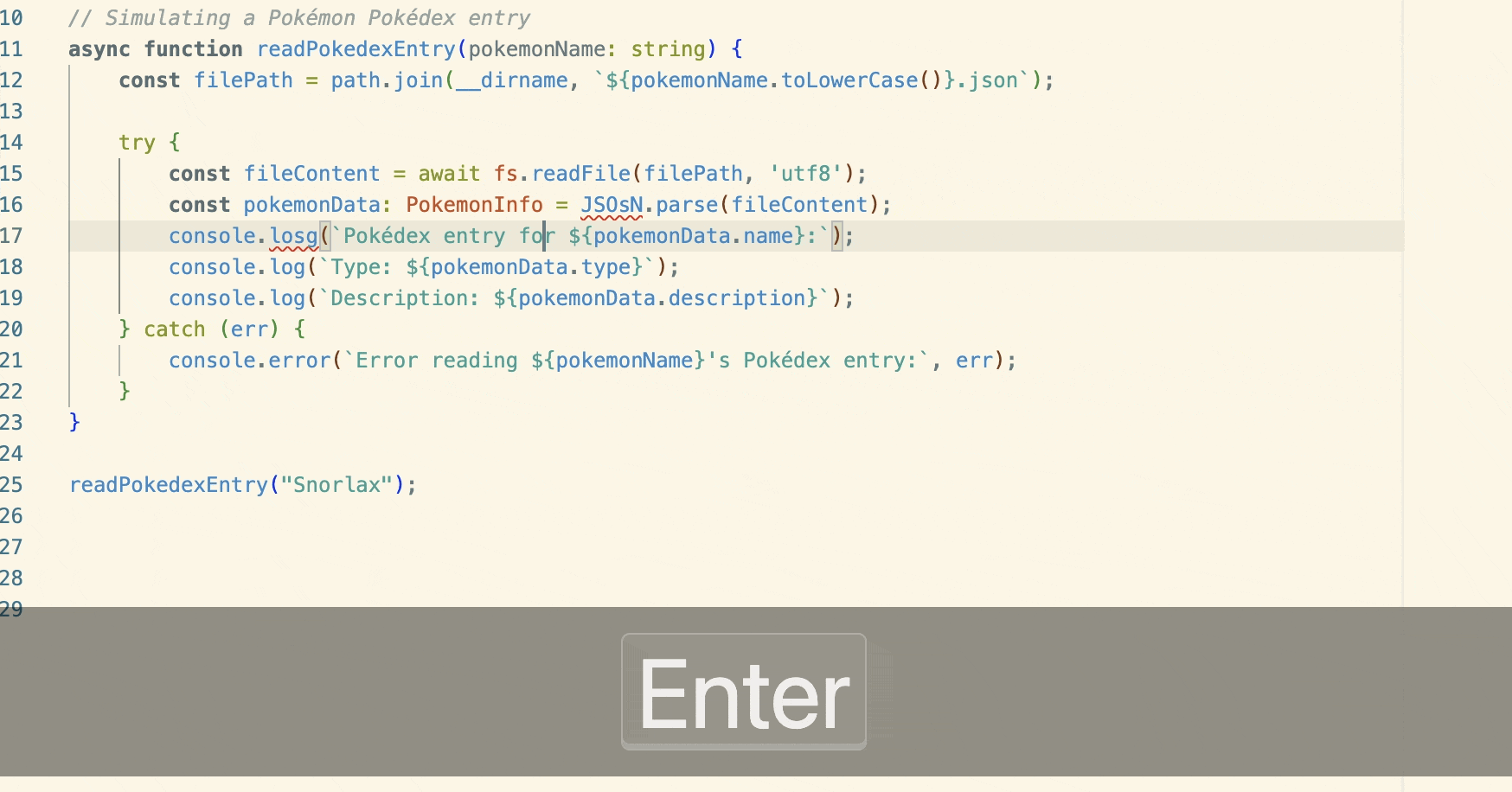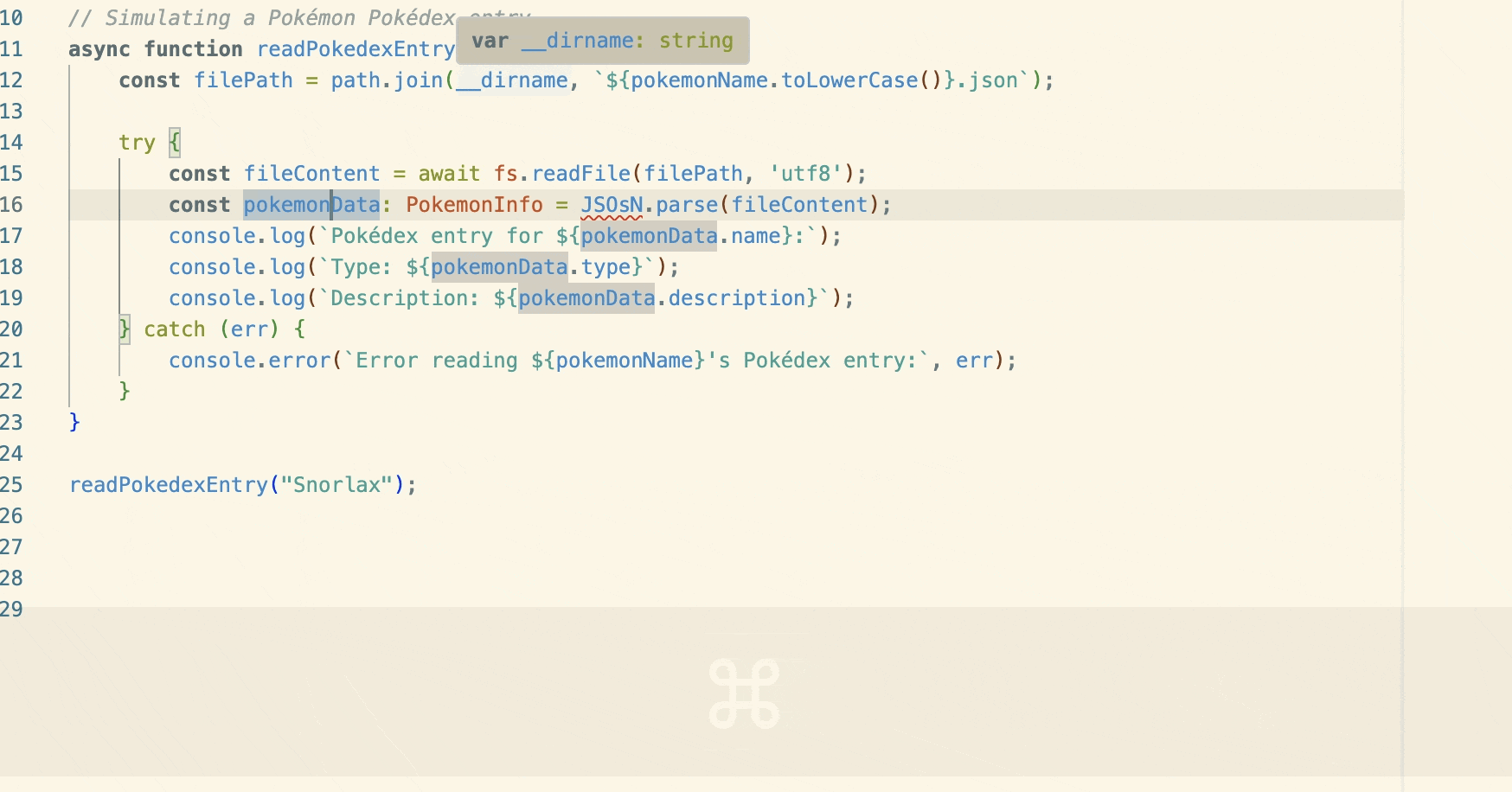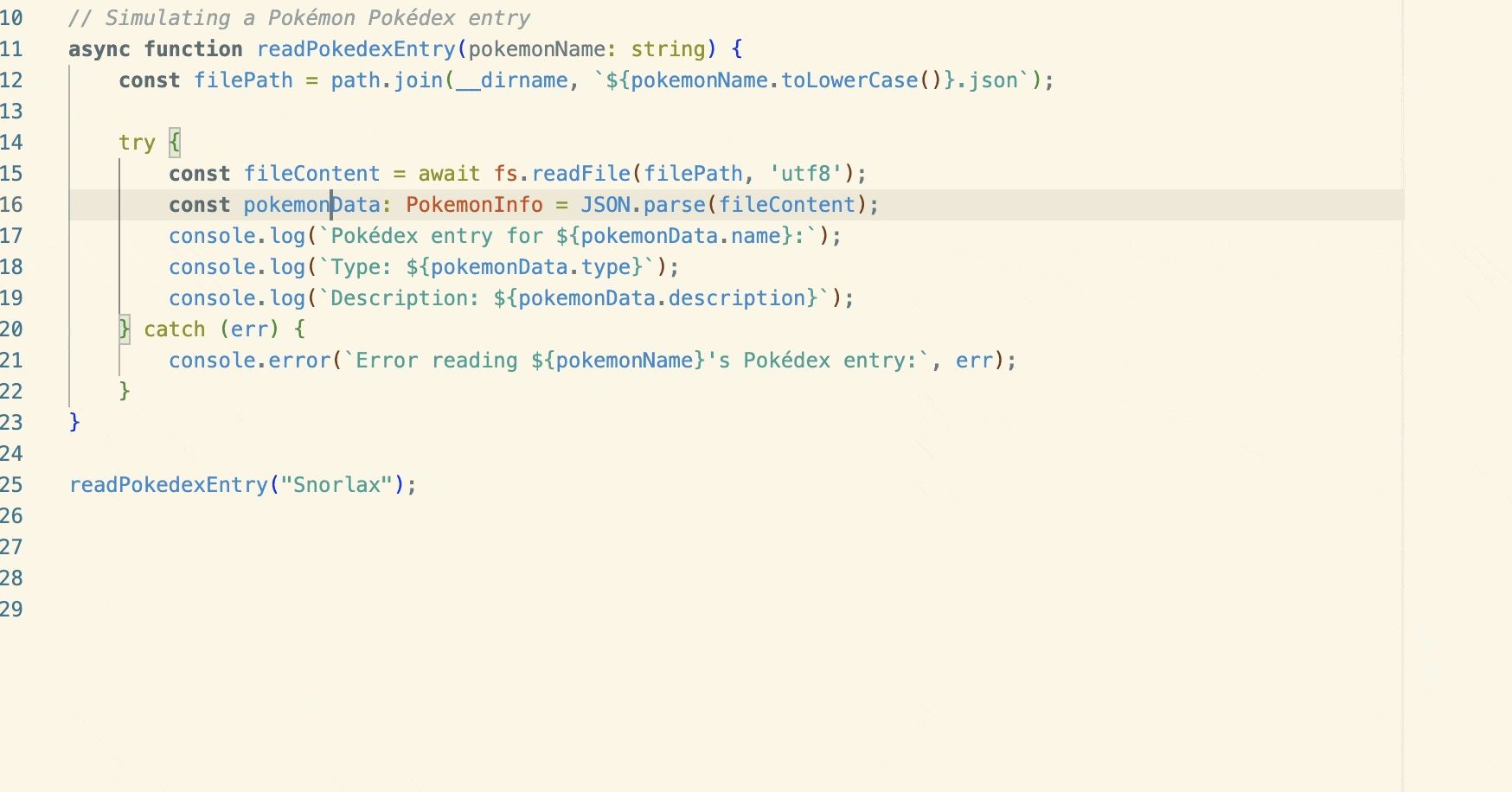
- 8.1.2 Chat agents
- 8.1.3 @workspace
- 8.1.4 Agents replace slash commands
- 8.1.5 Commit message generation
- 8.1.6 Import grouping
- 8.1.7 Improved /explain context
- 8.1.8 Persistent chat view state
- 8.1.9 Chat using configured display language
- 8.1.10 Reduce welcome message verbosity
- 8.1.11 Terminal Quick Fixes
- 8.1.12 Terminal command suggestions
- 8.1.13 Improved surfacing of Run in Terminal action
- 8.1.14 Inline chat can reply with terminal commands
- 8.2 Python
- 8.2.1 Improvements to run line in the terminal
- 8.2.2 Improvements to Python linting extensions
- 8.2.3 Deprecated built-in linting and formatting features
- 8.2.4 Create environment notification
- 8.2.5 Virtual environment deactivation helper
- 8.2.6 Improvements to test output
- 8.2.7 Platform-specific versions of the Python Debugger extension
- 8.2.8 Tensorboard extension
- 8.3 Jupyter
- 8.4 VS Code Speech
- 8.5 GitHub Pull Requests and Issues
- 8.1 GitHub Copilot
- 9 Preview Features
- 10 Extension authoring
- 11 Proposed APIs
- 12 Engineering
- 13 Extensions and documentation
- 14 Notable fixes
- 15 Thank you
Clear, format, and save opt-in audio cues
When audioCues.clear is enabled, a sound indicates that the terminal, a notification, or the chat responses have been cleared.
In files and notebooks, audioCues.save and audioCues.format can be set to play on user gesture or always for each event. While disabled, an ARIA alert is used instead and can be customized with accessibility.alert.format and accessibility.alert.save.
Windows magnifier synced
The windows magnifier now follows the cursor in VS Code properly.
Accessible View improvements
By default, a user’s cursor is positioned at the bottom of the terminal Accessible View; to preserve the position instead, you can set terminal.integrated.accessibleViewPreserveCursorPosition to true.
The Accessible View can be hidden with accessibility.hideAccessibleView, useful if sharing one’s screen with an audience of sighted users.
The Accessible View now closes when a user starts typing and focuses the prior element for a smoother work flow.
Text editor in window title focused view
Last iteration, we added a ${focusedView} variable to window.title. We now also indicate when a Text Editor is focused.
Workbench
Customize Activity bar position
You can now move the Activity bar to top of the Side Bar as shown in the following video.
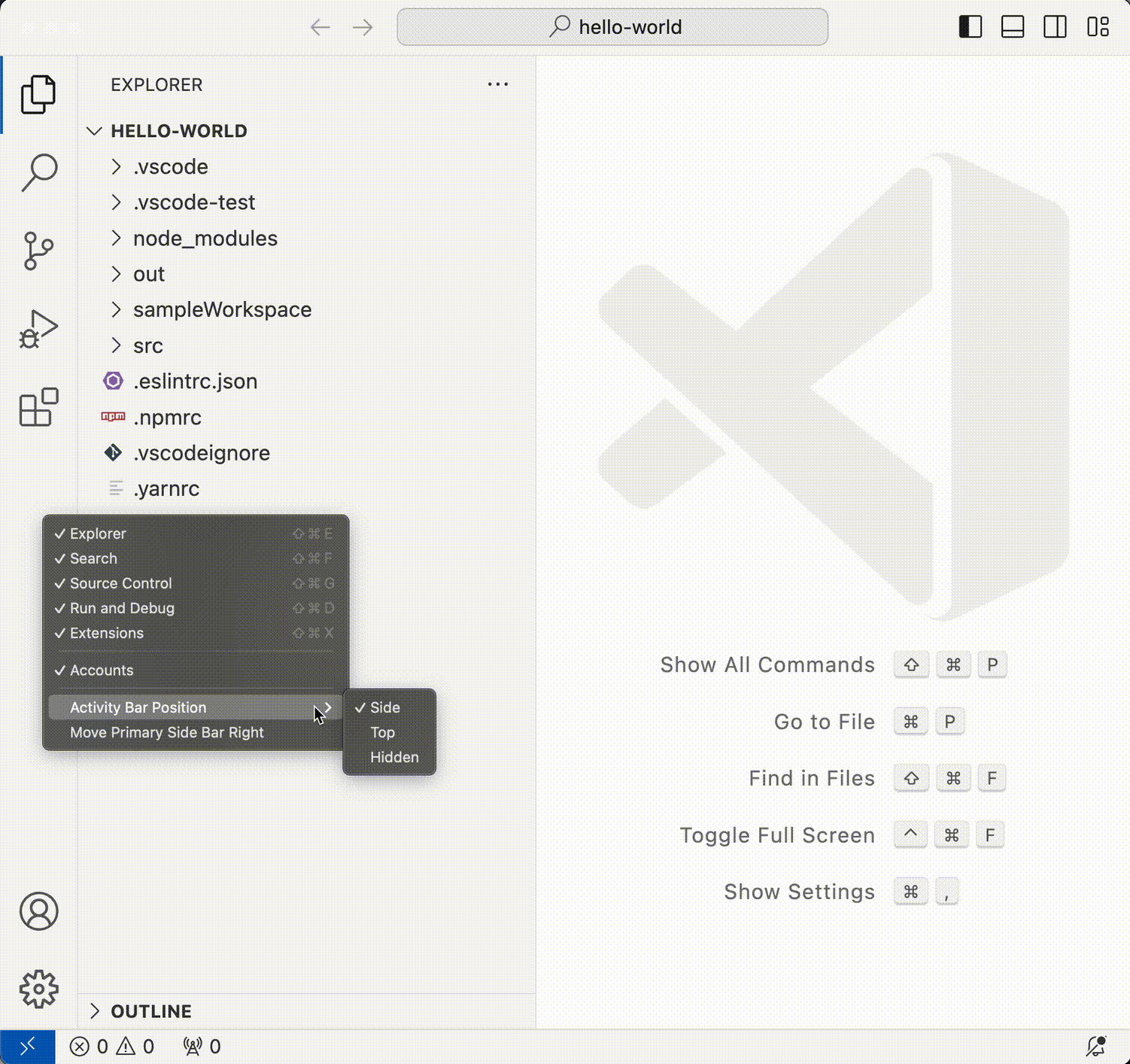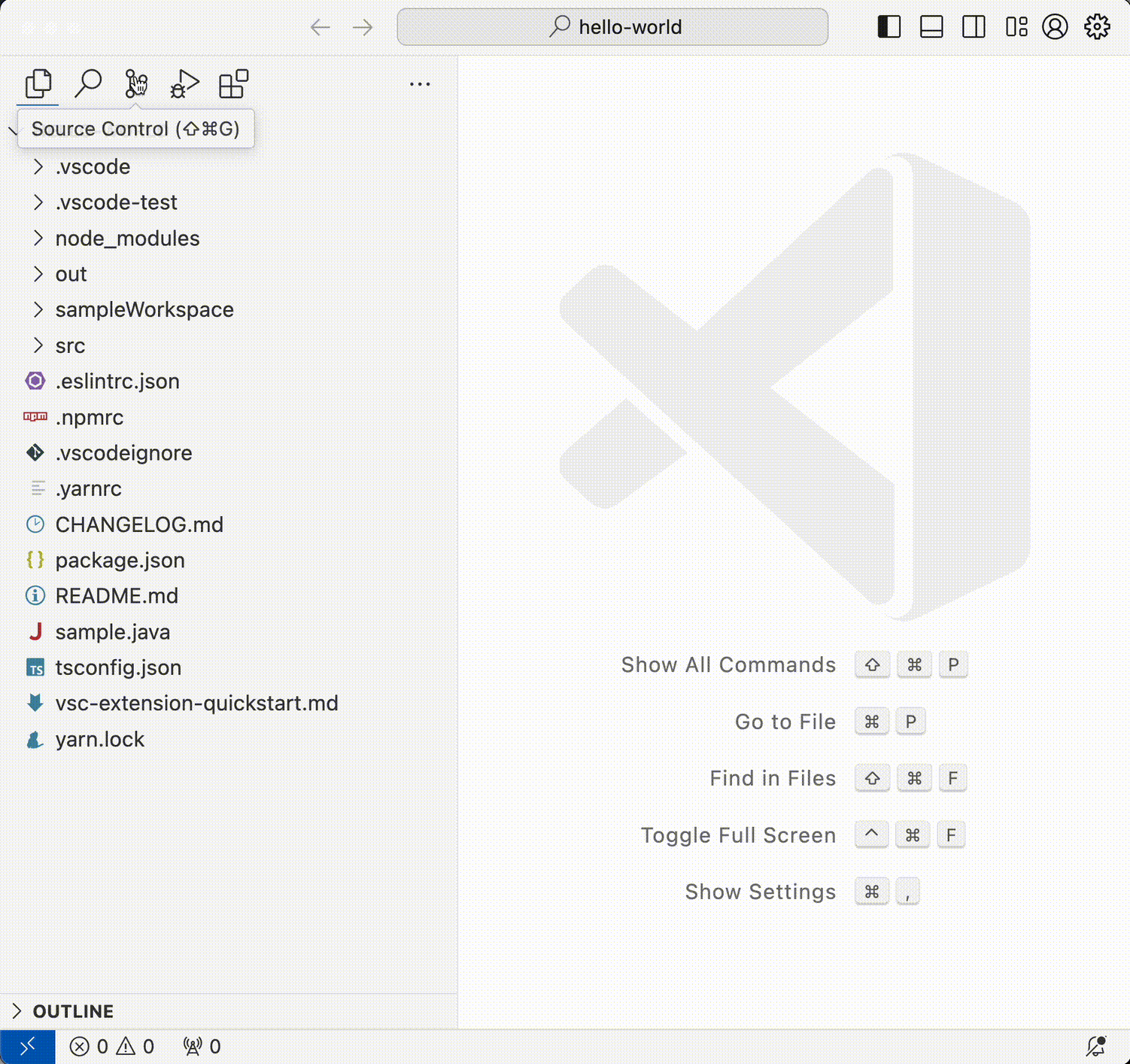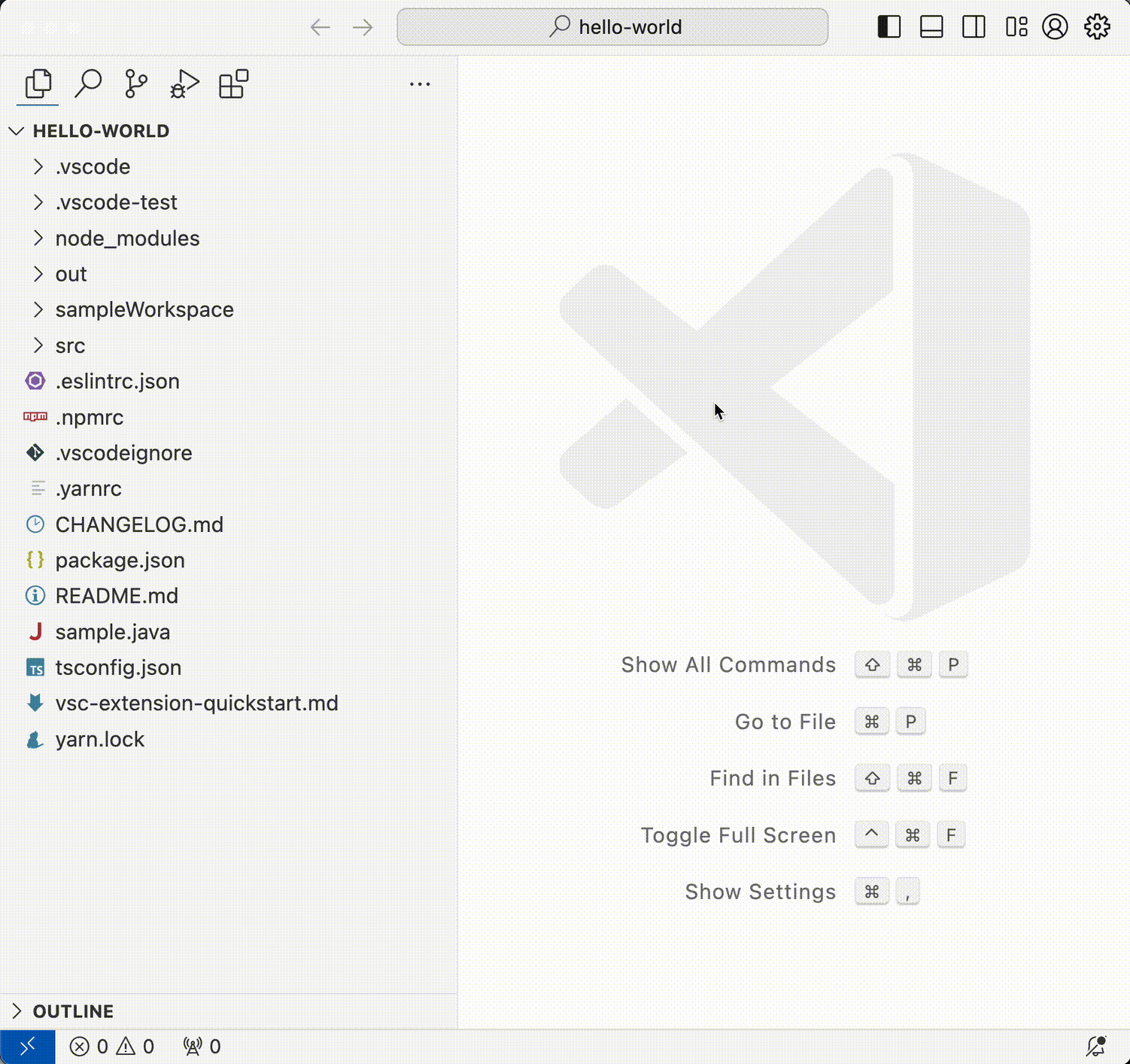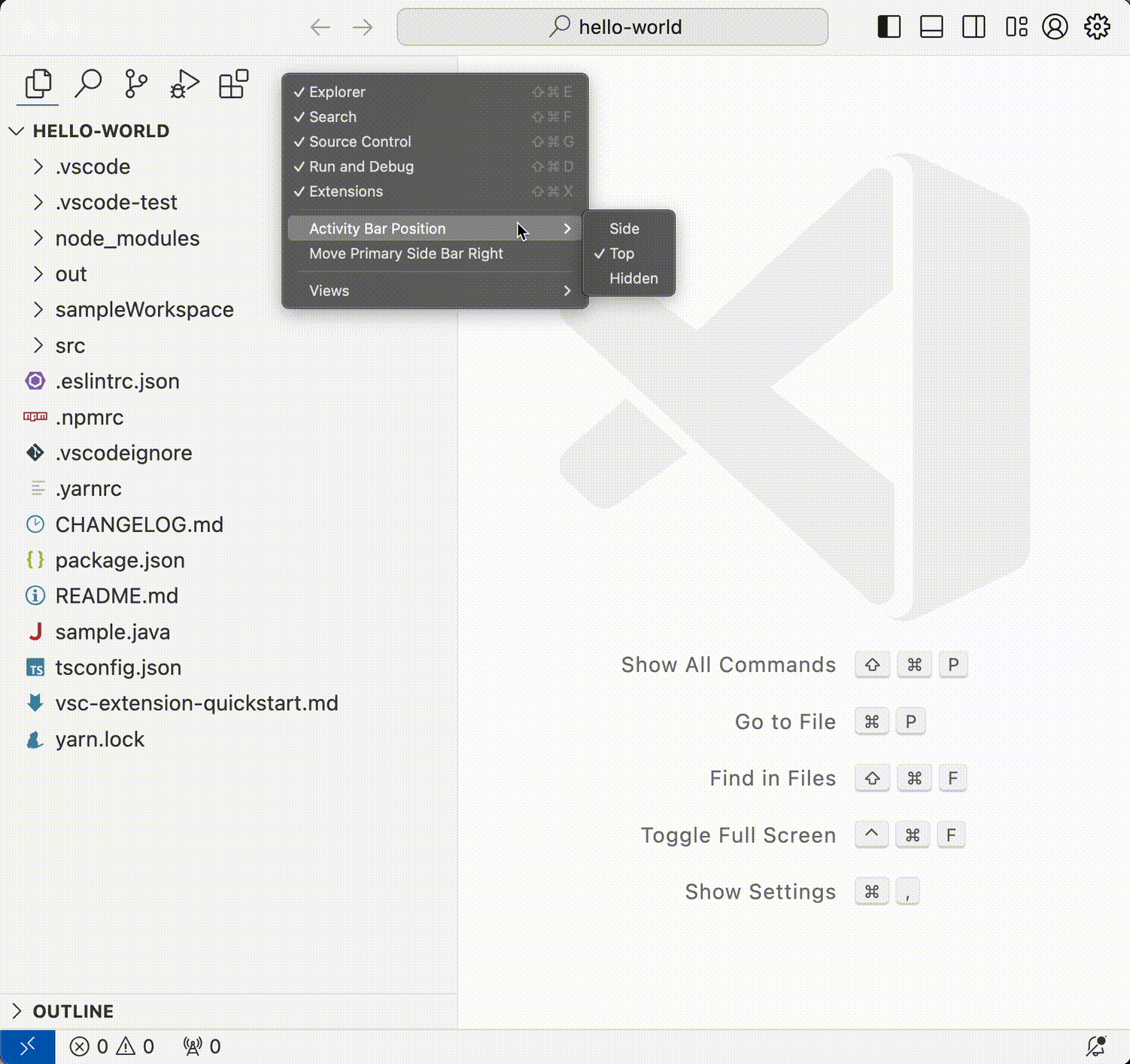
When the Activity bar is placed on the top, the Accounts and Manage buttons are moved to the title bar to the far right.
Note: This is supported only when the custom title bar is enabled ("window.titleBarStyle": "custom").
Hide Editor Tabs
Users are now able to hide editor tabs by setting workbench.editor.showTabs to none. Other showTabs options are multiple (default) and single to show a single editor tab for the active editor.
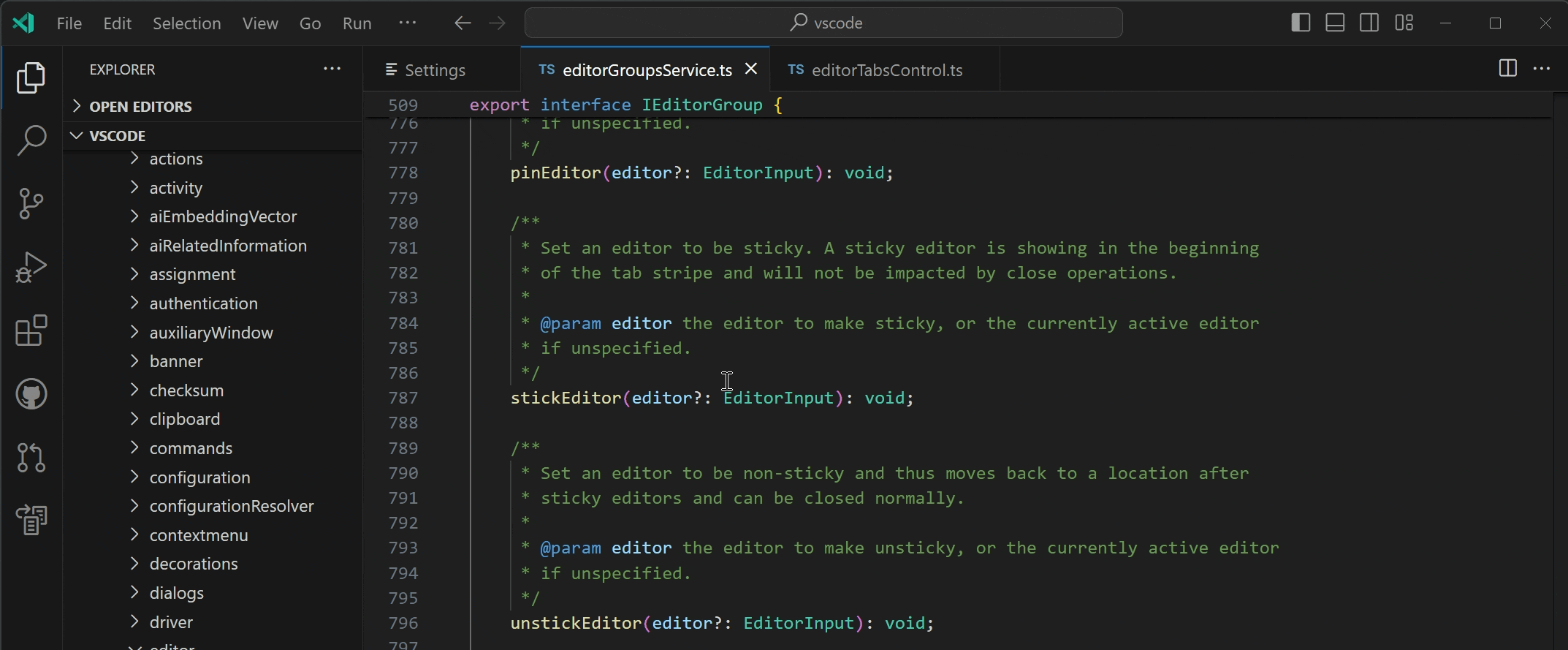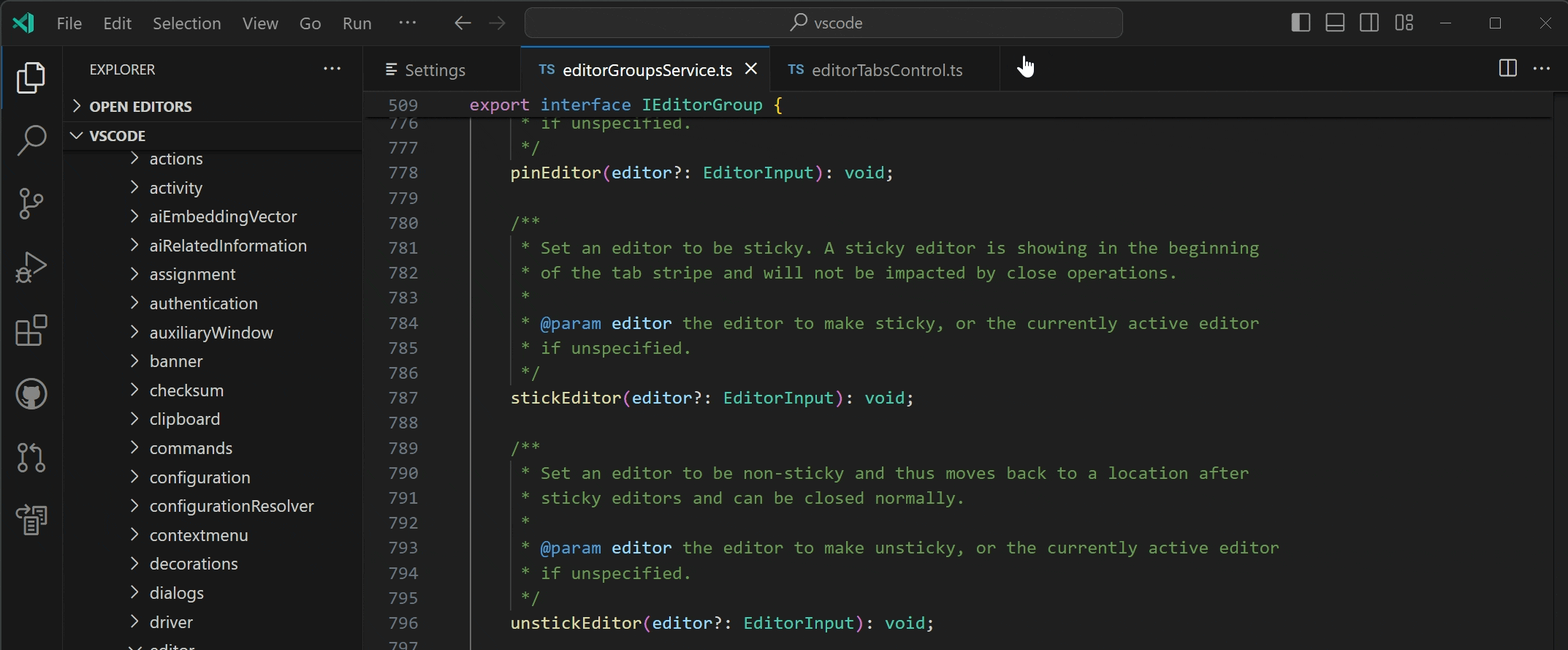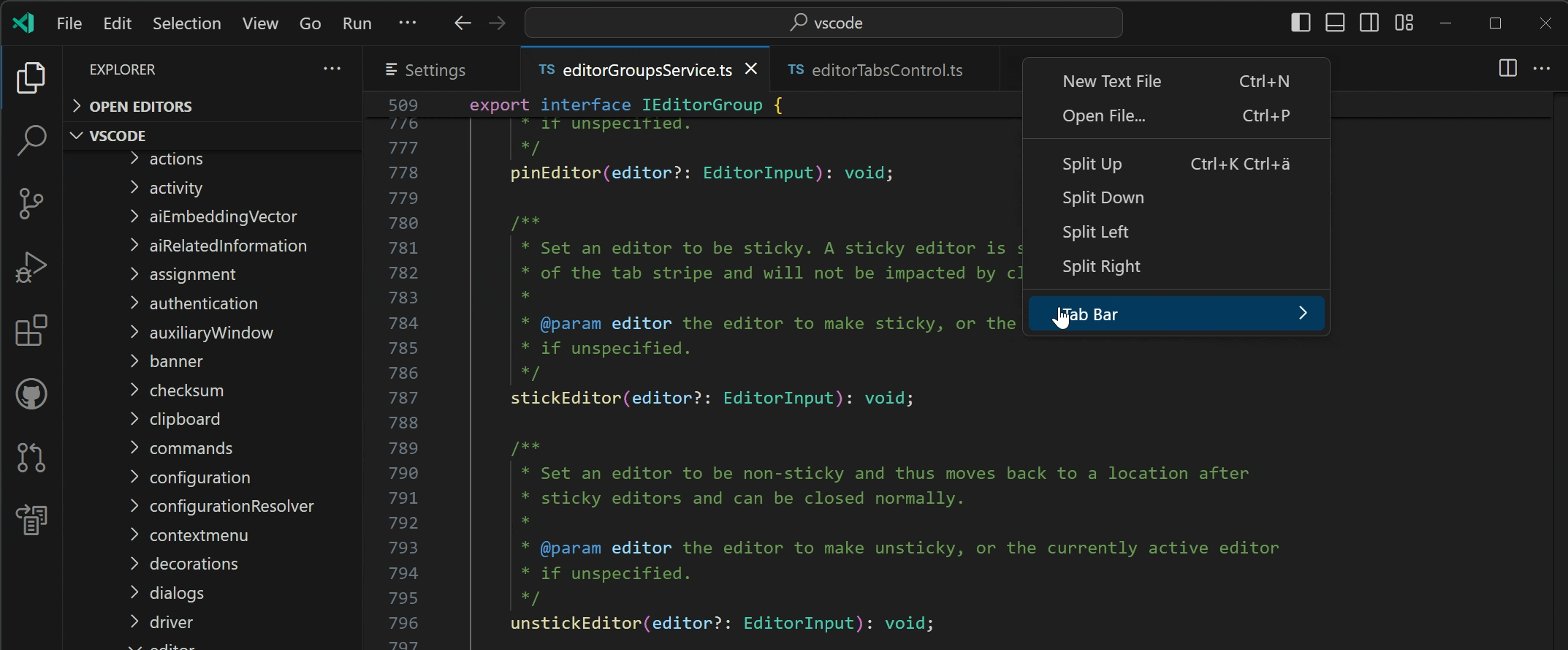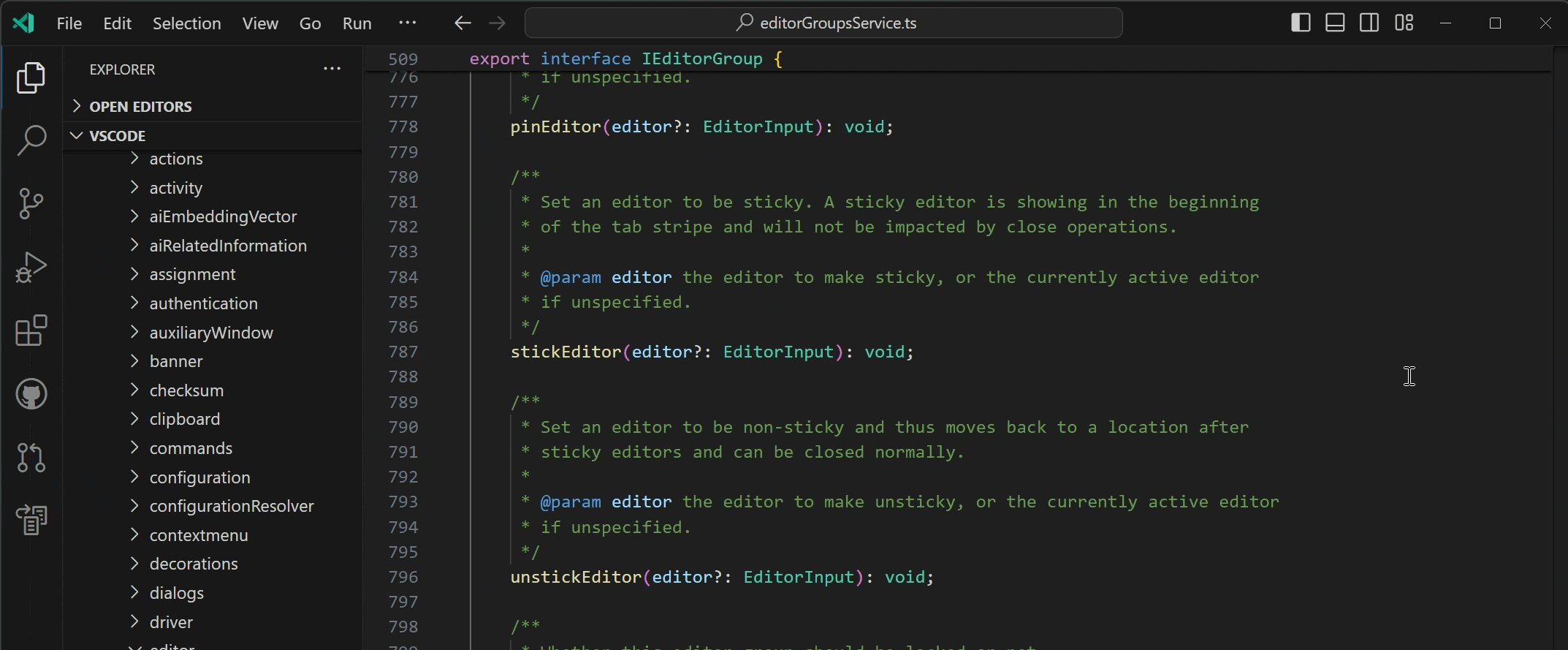
Maximize Editor Group
There is a new command View: Toggle Maximize Editor Group (⌘K ⌘M (Windows, Linux Ctrl+K Ctrl+M)) to maximize an editor group. This will hide all other groups and adds a button to the tab bar, allowing the user to restore the previous layout. If the setting workbench.editor.doubleClickTabToToggleEditorGroupSizes is set to maximize, users can double-click on an editor tab to maximize and unmaximize the editor group.
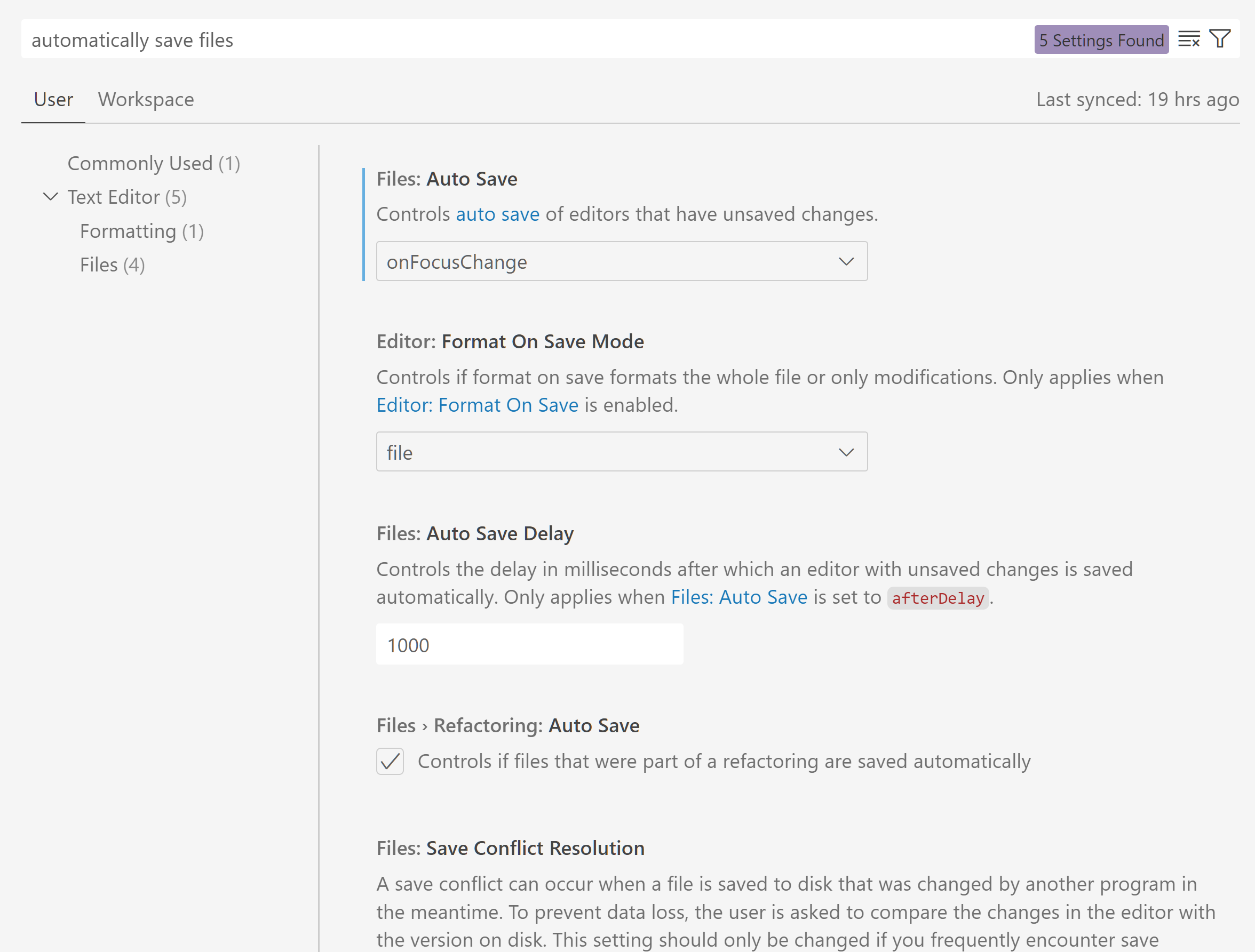
Similar settings search in the Settings editor
Like the Command Palette, the Settings editor now runs a similar settings search to gather more relevant results for a given query.
The implementation is currently in an early stage, and can expect improvements over the next few iterations.
Confirmation for opening protocol links
When a protocol link for a file or workspace opens in VS Code, a dialog will now ask for confirmation:
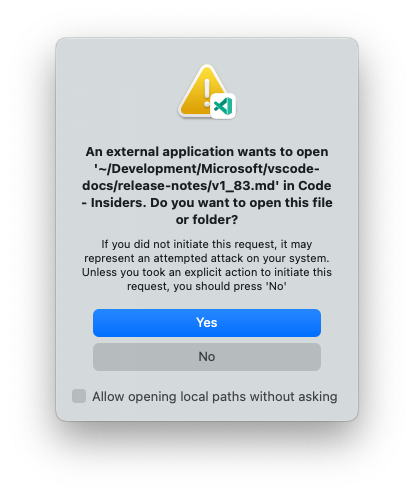
Protocol links can either point to a local file (for example vscode://file/path/to/file) or to a remote file (for example vscode://vscode-remote/ssh-remote+[USER@]HOST[:PORT]/path/to/file). For each case, there are new settings to disable this behavior:
security.promptForLocalFileProtocolHandling– For local protocol linkssecurity.promptForRemoteFileProtocolHandling– For remote protocol links
Editor
Nearest Quick Fix keyboard shortcut
There is a new setting to activate the nearest Quick Fix in a line from ⌘. (Windows, Linux Ctrl+.) (command ID editor.action.quickFix), no matter where your cursor is in that line. Previously a preview feature, Code Action Widget: Include Nearby Quick Fixes (editor.codeActionWidget.includeNearbyQuickFixes) is now enabled by default.
The command highlights the source code that will be refactored or fixed with Quick Fixes. Normal Code Actions and non-fix refactorings can still be activated at the cursor location.
Multi-document highlighting
Initial support for code highlighting across multiple documents was added via the setting Editor: Multi Document Occurrences (editor.multiDocumentOccurrencesHighlight). This initial implementation features only textual occurrences, with support for semantic highlighting coming in the future.
Source Control
Force push using –force-if-includes
This milestone there is now support for the --force-if-includes option, which is an auxiliary option to --force-with-lease added in Git 2.30. The new option ensures that commits that are being force-pushed were created after examining the commit at the tip of the remote reference, and reduces the chance of losing commits when auto fetch is enabled. You can disable the use of --force-if-includes by disabling the git.useForcePushIfIncludes setting.
Notebooks
Scroll on Execute improvements
How the next cells are revealed when executing through notebooks with Shift+Enter was improved to help focus on the output. This also reduces the amount of cell movement when re-executing cells that already have output.
IPython stack trace rendering
Exception stack traces from IPython now render clickable links to help navigate to the error. This will only apply if the Jupyter extension does not alter the stack trace first: "jupyter.formatStackTraces": false.
Debug
JavaScript Debugger
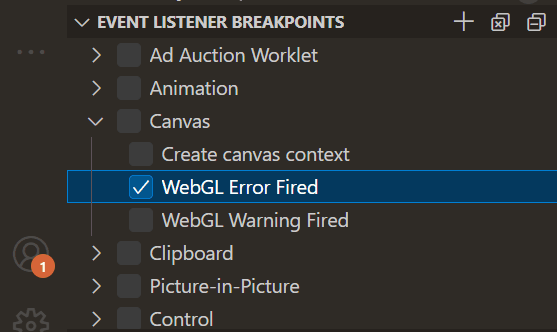
Improved Event Listener Breakpoints view
The Event Listener Breakpoints view is friendlier and is now presented as a tree with checkboxes:
Better handling of sourcemap renames
When code is compiled with a bundler, variables can be renamed. This is especially common with imports in all bundlers, and certain local identifiers in esbuild. The debugger is now aware of scopes each rename applies to, which fixes many snags users historically hit.
This requires the debugger to parse the syntax tree of compiled modules. This is done in a background thread and only when renames are detected, but the behavior can be disabled by setting "sourceMapRenames": false in your launch.json to avoid any performance impact.
Remote Development
The Remote Development extensions, allow you to use a Dev Container, remote machine via SSH or Remote Tunnels, or the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) as a full-featured development environment.
Highlights include:
- You can now log into Tunnels using your Microsoft account.
- Connect to Dev Containers over SSH and Tunnels now supported on Windows.
You can learn more about these features in the Remote Development release notes.
Contributions to extensions
GitHub Copilot
Streaming inline chat
The GitHub Copilot Chat extension’s inline chat can now make progressive text edits and “types” at the rate at which a response being received. This is a more natural experience than the previous behavior of waiting for the entire chat response to be received before applying it to the editor.
Not all edits are insertions, and for replacements Copilot sometimes has a hard time figuring out where to start. In those cases, streaming might not yet work as expected. Stay tuned for improvements in this area.
Chat agents
This iteration, we built a new way to interact with Copilot Chat: agents. Agents are like experts who have a specialty that they can help you with, and you can talk to them in the chat by mentioning them with the @ symbol. Currently, there are two agents:
@workspacehas context about the code in your workspace and can help you navigate it, finding relevant files or classes.@vscodeknows about commands and features in the VS Code editor itself, and can help you use them.
Each agent also supports a few slash commands, and the slash commands that you may have used before should now be used with an agent. For example, /explain is now @workspace /explain. But as a shortcut, you can also just type / for a list of completions that will automatically expand to the full agent and command.
@workspace
The @workspace agent uses a meta prompt to determine what information to collect from the workspace to help answer your question. One approach used by the meta prompt is to look back at your conversation history to resolve ambiguous words/phrases in a question. For example, if you ask @workspace What does it do?, the meta prompt will now consider the history to figure out what it actually is and what information to collect to answer the question. The meta prompt also uses a wide set of terms, including more synonyms, to generate a list of potentially relevant terms.
File paths and symbols in @workspace responses are clickable links. This makes it easy to navigate to the code that Copilot is referring to.
The @workspace agent respects the .gitignore and .copilotignore when deciding which files from the workspace to index.
Agents replace slash commands
The new agents replace the functionality of slash commands such as /createWorkspace and /createNotebook with added slash modifiers:
/createWorkspace–>@workspace /new/createNotebook–>@workspace /newNotebook/explain–>@workspace /explain/fix–>@workspace /fix/test–>@workspace /test/vscode–>@vscode /api
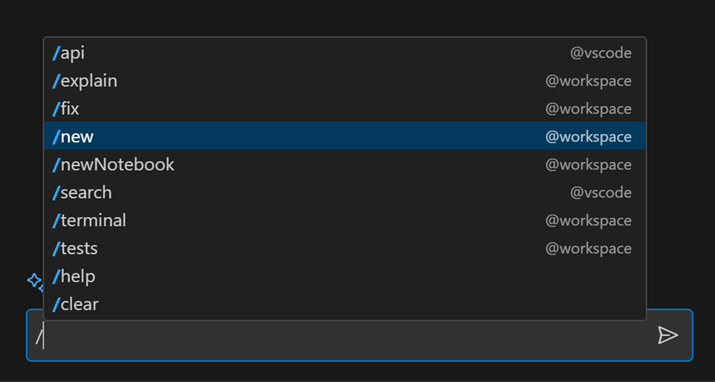
Try out the new agents, and type /help for more tips!
Commit message generation
Copilot Chat can now generate commit messages based on the pending changes using the new “sparkle” action in the Source Control input box.
Import grouping
Generated imports are now always put to the top of the file or below existing import blocks. This is supported for most common programming languages.
Improved /explain context
You can ask Copilot Chat to explain a code selection in your active editor either through the @workspace /explain command or through the Explain with Copilot action in the context menu. Copilot Chat now includes the implementations of referenced symbols such as functions and classes, leading to more accurate and useful explanations. This works best across files when you have an extension contributing language services installed for one of the following languages: TypeScript/JavaScript, Python, Java, C#, C++, Go, or Ruby.
Persistent chat view state
Previously, the Copilot Chat view was initially hidden and then later shown. The Copilot Chat view now remains active between window reloads so you don’t have to manually reopen it. Additionally, the Chat view now guides you through the process of signing into GitHub and activating your free trial of GitHub Copilot.
Chat using configured display language
By default, Copilot Chat now initially responds using your configured display language in VS Code. You can override this automatic behavior by configuring github.copilot.chat.localeOverride.
Reduce welcome message verbosity
You can now control whether Copilot Chat greets you with a verbose welcome message when you first start a conversation by configuring github.copilot.chat.welcomeMessage. The options are first (default), always, and never.
Terminal Quick Fixes
When a failed command is run in the terminal, Copilot will now offer a Quick Fix to explain what happened.
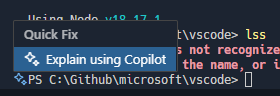
This can be triggered via the sparkle icon (⌘. (Windows, Linux Ctrl+.)) next to the current terminal prompt.
Terminal command suggestions
Copilot can now offer CLI command suggestions via the ⌘I (Windows, Linux Ctrl+I) keybinding when the terminal is focused. This brings up Quick Chat with @workspace /terminal pre-filled:
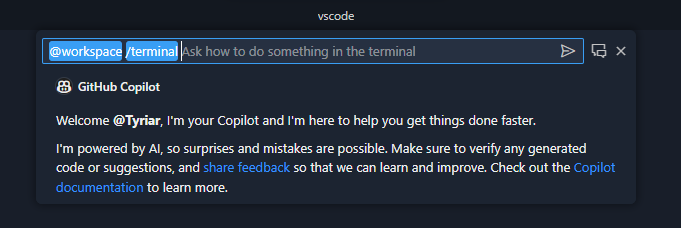
This /terminal slash command is optimized for suggesting shell commands using the current shell. The quality of suggestions and UX will see more improvements next release.
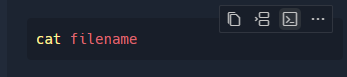
Improved surfacing of Run in Terminal action
When a code block has a shell language type, the Run in Terminal action is now surfaced on hover of the code block:
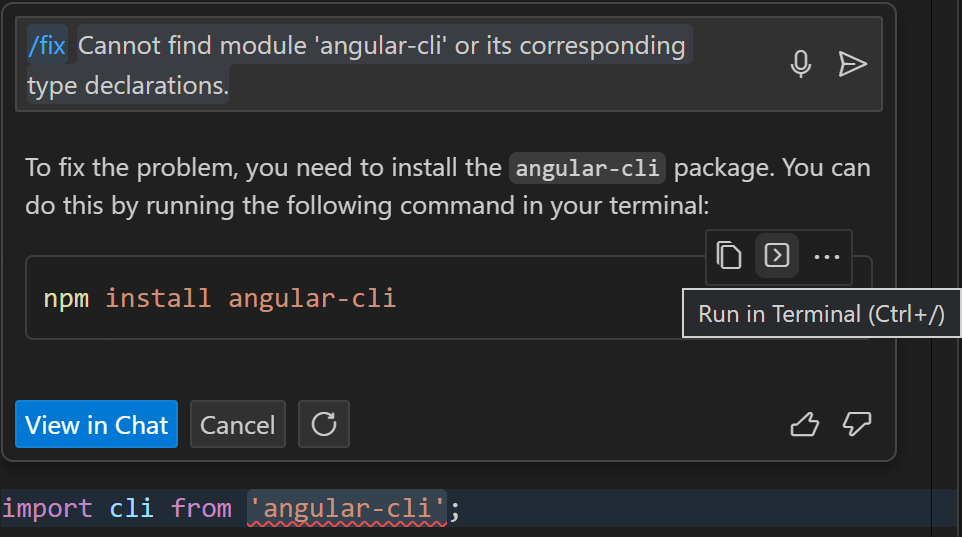
Inline chat can reply with terminal commands
The inline chat can now reply with commands to be run in the terminal:
Python
Improvements to run line in the terminal
The Python extension has improved the behavior of sending lines to the Python REPL (Shift+Enter) when no code has been selected to run. Previously, when you placed the cursor on a line of Python code and pressed Shift+Enter, the Python extension would send the exact line content to the REPL, even if it would fail, for example, due to being part of a multi-line command.
With the new experimental Smart Send feature, the Python extension sends the smallest block of runnable code surrounding the cursor position to the REPL for execution. This ensures that only complete and executable sections of code are sent to the REPL. The cursor will also be automatically moved to the next executable line, to provide a smooth experience when executing multiple chunks iteratively.
To try it out, you can add the following User setting: "python.experiments.optInto: ["pythonREPLSmartSend"]. While this feature is currently behind an experiment, we expect it to be the default behavior in the future. If you have feedback or suggestions on how we can further improve this feature, please let us know!
Theme: Catppuccin Macchiato (preview on vscode.dev)
Improvements to Python linting extensions
We have made several improvements to our supported linting extensions to allow for a more configurable and flexible experience with your favorite Python tools.
The Pylint, Mypy and Flake8 extensions now offer settings that allow you to specify glob patterns for files that you wish to exclude from linting. This can be useful if you are working with a large codebase with many subprojects, and want to exclude certain folders from being linted. These settings are "pylint.ignorePatterns", "mypy-type-checker.ignorePatterns" and "flake8.ignorePatterns".
These extensions also support cwd settings, which allows you to specify the working directory for the linter. This setting has been updated to support the variable ${fileDirname}, so the working directory can be dynamically set to the parent folder of the file you have open in the editor. This is useful if you are working with mono repos, and want the linter working directory to be dynamically updated as you open files from different subprojects. These settings are "pylint.cwd", "mypy-type-checker.cwd" and "flake8.cwd".
The default value of the "mypy-type-checker.preferDaemon"setting was changed (only applicable to the Mypy extension). Previously, it was set to true, which meant that the Mypy daemon would be used by default. After receiving feedback, we changed the default value to false. If you are wondering which value would best for you, our recommendation is to use the Mypy daemon if you enabled the Mypy reporting scope to be the entire workspace ("mypy-type-checker.reportingScope": "workspace") for performance reasons. Otherwise, if the reporting scope is set to the current file, we recommend you use the Mypy executable that shipped with the extension.
Deprecated built-in linting and formatting features
With all the work and improvements made to the linting and formatting extensions in VS Code, we have deprecated the built-in linting and formatting features that are shipped in the Python extension. This includes all the linting and formatting commands as well as settings (python.linting.* and python.formatting.*). We recommend you remove these deprecated settings if you are still using them, and use the supported linting and formatting extensions instead.
If you are using a linter without a supported extension, check out the community-contributed Ruff extension. Ruff is a Python linter written in Rust and supports various linters such as pyflakes, pycodestyle, pydocstyle, and more. Recently support was added for using Ruff as a formatter in VS Code ("[python]": { "editor.defaultFormatter": "charliermarsh.ruff" }).
You can also create your own linter or formatter VS Code extension for your favorite Python tool. Check out our Python Tools Extension Template for a quick start.
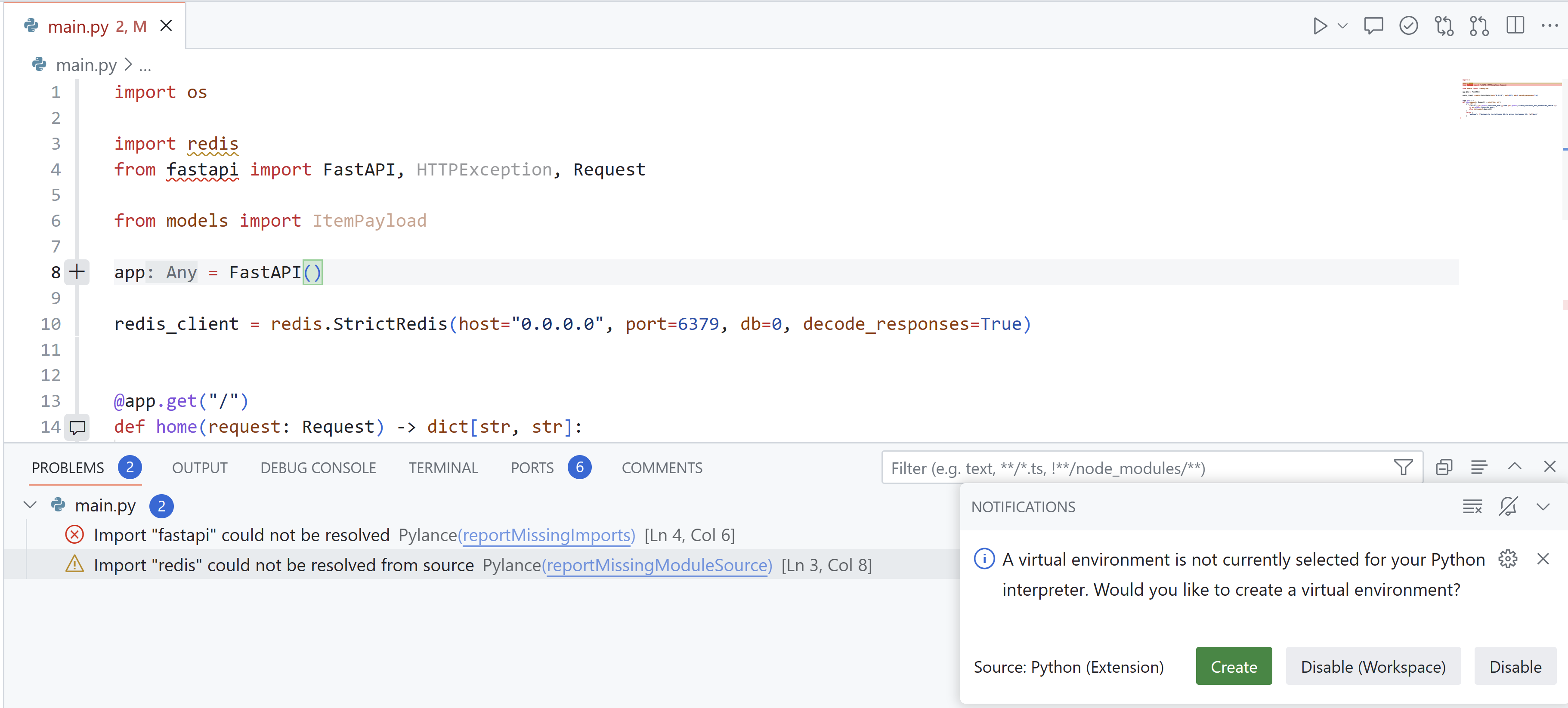
Create environment notification
Virtual environments are a recommended way to work with Python projects with dependencies that need to be installed. They offer isolation and reproducibility and are very popular in Python projects.
For this reason, the Python extension now displays a notification when you attempt to run or debug a Python file or project with listed dependencies when you don’t have a virtual environment selected on your workspace. This notification provides a quick way to create a new virtual environment through the Python: Create Environment command.
If you already have a virtual environment on your workspace, you have the option to select it, or delete and recreate it.
This notification can be disabled by setting python.python.createEnvironment.trigger to off.
Virtual environment deactivation helper
A couple of months ago we announced a new experimental feature for terminal activation using environment variables, to enhance your development workflow by automatically activating the selected environment in the terminal without the need for explicit activation commands. However, since there are no explicit activation scripts working, the deactivate command was no longer working when this experiment was enabled.
The Python extension will now detect when you attempt to run the deactivate command and show a helper notification to guide you on how to add scripts for your shell so the command will work again when the environment is activated through environment variables. It also offers a button to open your shell profile file for you to add the necessary scripts.

You can find the full documentation on how to add the necessary scripts for your shell on the vscode-python wiki.
If you are not in the experiment and would like to try out this feature, you can add the following User setting: "python.experiments.optInto: ["pythonTerminalEnvVarActivation"].
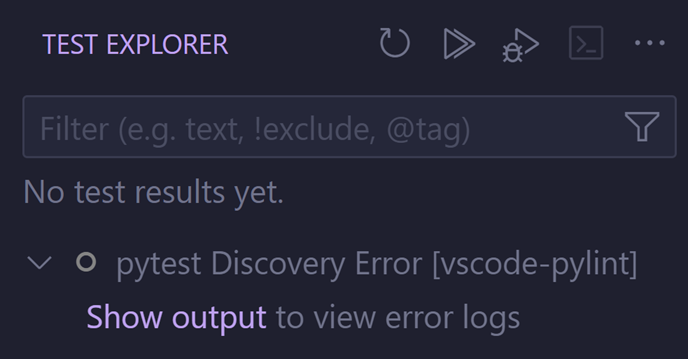
Improvements to test output
We’ve made significant improvements to how you can view and interact with the test output in the Python extension when the pythonTestAdapter experiment is enabled, announced a few months ago. Previously, output from test discovery and execution was inconsistently scattered across the Python Test Log output channel and the Test Results panel, with some information being duplicated in both. To consolidate the experience, output related to test execution is displayed in the Test Results panel, and test discovery in the Python output channel. To learn more, read our related vscode-python wiki.
This new approach also supports colorization in the output if you are using Pytest and set "python.testing.pytestArgs": ["--color=yes"] in your settings.json. Colorization only works for test execution in the Test Results panel and will not work for discovery or for output in the Python Test Log panel.
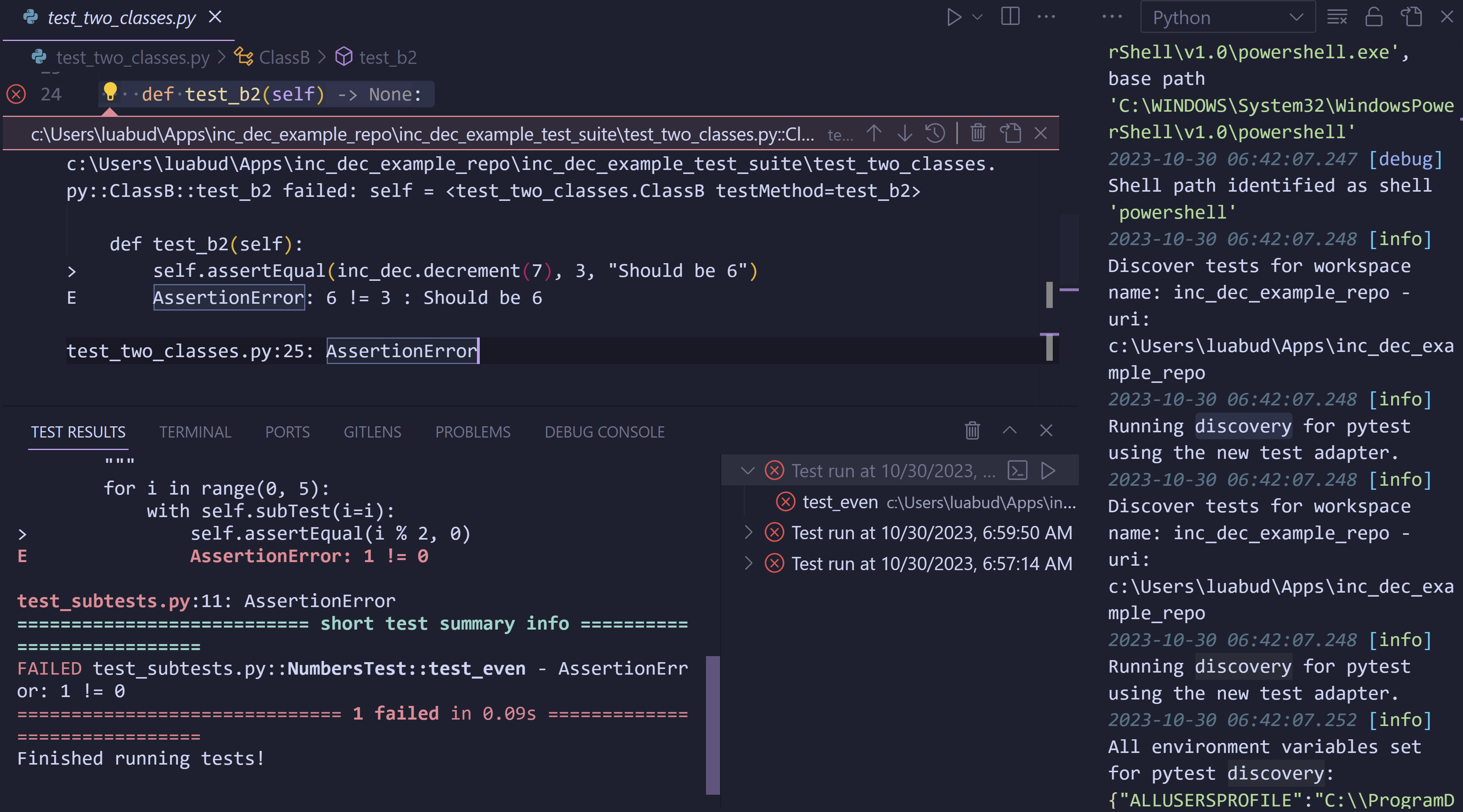
There is also a new button Show output to easily open the Test Logs from the Test Explorer view when errors on test discovery occur.
Platform-specific versions of the Python Debugger extension
The Python Debugger extension now ships platform-specific versions, so that only the necessary platform-specific files are installed on every update. This reduces the size of the extension and helps improve startup time.
Tensorboard extension
The Tensorboard functionality has moved out of the Python extension into a standalone Tensorboard extension.
If you have any issues with this new extension or wish to provide feedback, you can file an issue in the Tensorboard extension GitHub repo.
Jupyter
Execute with Precedent/Dependent Cells
With the Jupyter extension, you can now run all precedent or dependent cells of a target cell from the dropdown menu next to the Cell Run button. This is still a preview feature and can be enabled with the jupyter.executionAnalysis.enabled setting and the notebook.consolidatedRunButton setting.
This feature is currently powered by the Pylance extension so you will need to install the latest Prerelease version of Pylance to use this feature.
VS Code Speech
We are introducing a new extension to bring voice support to VS Code! The new VS Code Speech extension integrates into GitHub Copilot Chat to enable voice-to-text transcription services for Chat input.
Once installed, a microphone icon appears and when selected, begins filling Chat input with text based on the transcribed results of your voice. The transcription is computed locally on your machine and does not require a connection to the internet.
GitHub Pull Requests and Issues
There has been more progress on the GitHub Pull Requests and Issues extension, which allows you to work on, create, and manage pull requests and issues.
- Projects are displayed and can be added from the Pull Request description webview.
- Integrated with GitHub Copilot to generate the PR title and description from the PR Create view.
- PRs checked out with the GitHub CLI (
gh pr checkout) are recognized by the extension.
Review the changelog for the 0.76.0 release of the extension to learn about the other highlights.
Preview Features
Floating editor windows
We continued exploring how to pull editors out of the workbench window into their own windows and now want to invite the VS Code Insiders community to play with this exciting new feature and provide feedback.
Make sure to install VS Code Insiders and run the new View: Move Active Editor into a New Window command on editors to open them in a floating window.
We still have to figure out many issues and provide missing features, but we are optimistic that we can enable this feature in Stable in the near future.
Thanks for testing!
WASM-WASI support for Language Servers
Support for language servers in WASM/WASI was added to the experimental wasm-wasi-core extension.
There is also an extension showcasing a simple language server written in Rust and compiled to WASM in the vscode-wasm repo. The extension depends on the language server crate maintained by the Rust analyzer team.
Improved test runner
There is now a command-line runner and extension for VS Code to make running tests for extensions easier. Extensions using the new approach can run in VS Code’s testing UI. While some migration is required, this usually only takes a few minutes. Read the VS Code Testing Extensions documentation for more information.
Finalized TestMessage.contextValue API
You can provide a contextValue on TestMessages to be shown when users take actions on those messages. Additionally, two new menu contributions points are available, testing/message/context and testing/message/content. The former is displayed on the message in the Test Results tree view, and the latter is displayed over the message in the editor. For example, this might be used to provide an action to update a fixture in snapshot testing:
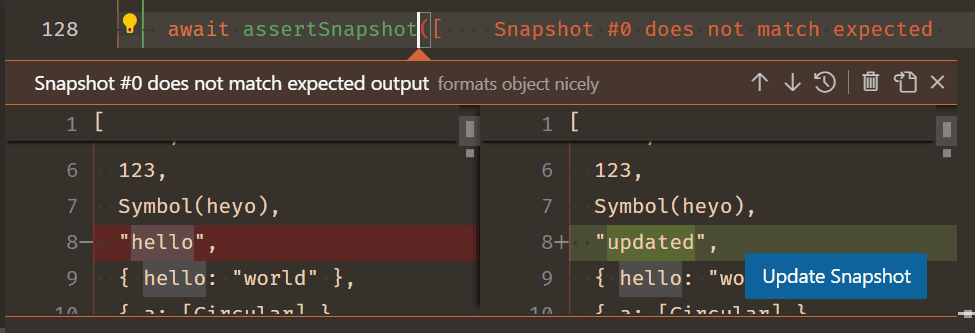
Read more about contextValue in issue #190277.
Updated codicons
The following new icons were added to our codicon library:
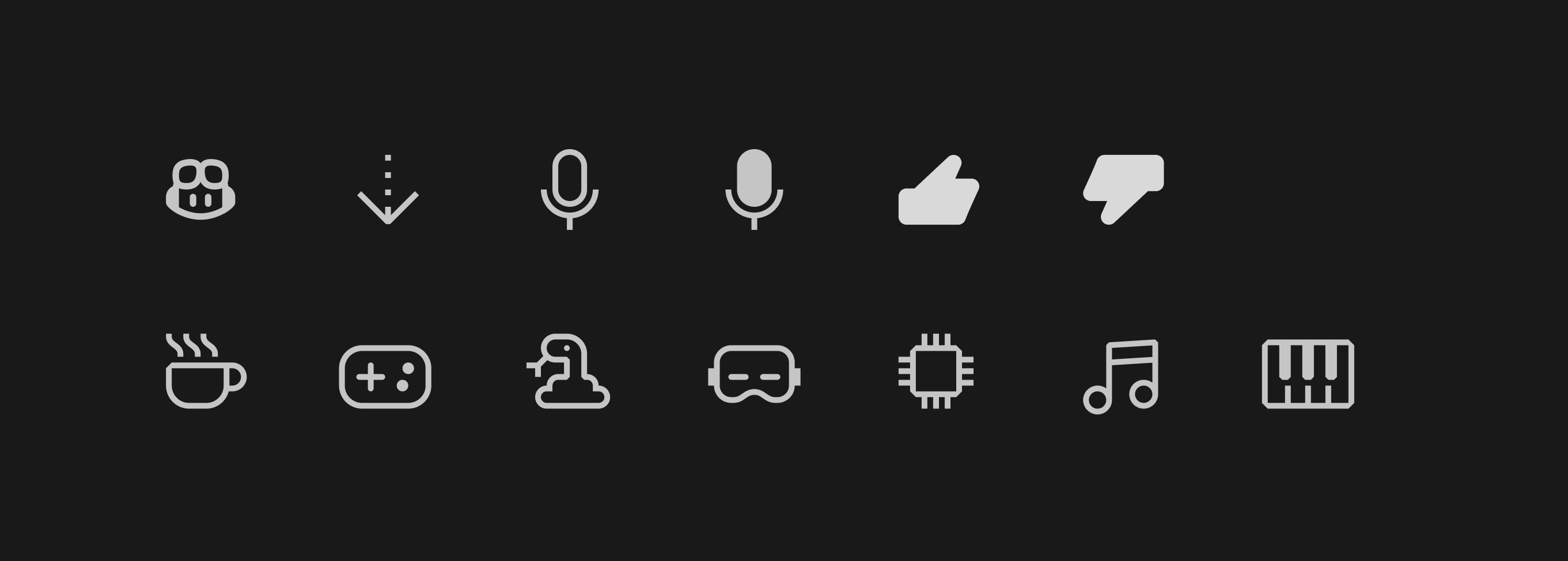
copilotgit-fetchmicmic-filledcoffeesnakegamevrchippianomusicthumbsup-filledthumbsdown-filled
New theme colors
textPreformat.background: Background color for preformatted text segments
Root folder icons per name
File icon themes authors can now define name specific icons for root folders using the new properties rootFolderNames and rootFolderNamesExpanded. You can review the File Icon Theme guide for more information.
Proposed APIs
Every milestone comes with new proposed APIs and extension authors can try them out. As always, we want your feedback. Here are the steps to try out a proposed API:
- Find a proposal that you want to try and add its name to
package.json#enabledApiProposals. - Use the latest @vscode/dts and run
npx @vscode/dts dev. It will download the correspondingd.tsfiles into your workspace. - You can now program against the proposal.
You cannot publish an extension that uses a proposed API. There may be breaking changes in the next release and we never want to break existing extensions.
Support configuring data sent to extensions via Issue Reporter
A new proposed API lets extension authors send additional data via the Issue Reporter.
export interface IssueUriRequestHandler {
// Handle the request by the issue reporter for the Uri you want to direct the user to.
handleIssueUrlRequest(): ProviderResult<Uri>;
}
export interface IssueDataProvider {
// Provide the data to be used in the issue reporter.
provideIssueData(token: CancellationToken): ProviderResult<string>;
// Provide the template to be used in the description of issue reporter.
provideIssueTemplate(token: CancellationToken): ProviderResult<string>;
}
export namespace env {
export function registerIssueUriRequestHandler(
handler: IssueUriRequestHandler
): Disposable;
export function registerIssueDataProvider(provider: IssueDataProvider): Disposable;
}
You can provide a URI via handleIssueUrlRequest to have the extension issue filed externally on GitHub, or provide a template string and extension data string for provideIssueData and provideIssueTemplate in order to send additional extension data to GitHub via the Issue Reporter.
Read more about this proposal in issue #196863.
File watchers with custom exclude rules
This milestone we added a proposed API for creating file system watchers with full control over exclude rules:
export interface FileSystemWatcherOptions {
/**
* An optional set of glob patterns to exclude from watching.
* Glob patterns are always matched relative to the watched folder.
*/
readonly excludes?: string[];
}
export function createFileSystemWatcher(
pattern: RelativePattern,
options?: FileSystemWatcherOptions
): FileSystemWatcher;
This new API gives your extension full control over the file watcher, irrespective if it’s a recursive or non-recursive watcher or whether it wants to watch inside or outside the workspace. User or default configured exclude rules for file watching will not apply, so you can be sure to receive only the events you subscribed to.
Engineering
Windows 32-bit support ends
There is no longer support for Windows 32-bit VS Code. If you’re still on 32-bit build of VS Code, you should update to the 64-bit version.
Extensions and documentation
Gradle for Java
Java development in VS Code just got easier with the improved Gradle for Java extension. The pre-release version has better support for building Gradle projects thanks to adopting the Build Server Protocol (BSP). Similar to other protocols used in VS Code, for example the Language Server Protocol (LSP), the BSP provides an abstraction layer between development environments and build tools such as Gradle.
To try out the new Gradle support, install both the Extension Pack for Java and pre-release version of the Gradle for Java extension. You can learn more about Gradle and the BSP in this recent blog post from the Java extension team.

FastAPI tutorial
FastAPI is a modern and fast web framework for building Python APIs, and has become more and more popular thanks to its simplicity and performance.
You can now learn how you can get the best out of VS Code and the Python extension to create and debug FastAPI applications through our new FastAPI Tutorial!
Custom Layout user guide
There is a new Custom Layout article describing layout customization for the workbench and editors. There you’ll learn how to modify VS Code’s main UI elements such as views, panels, and editors to fit your preferred workflow.
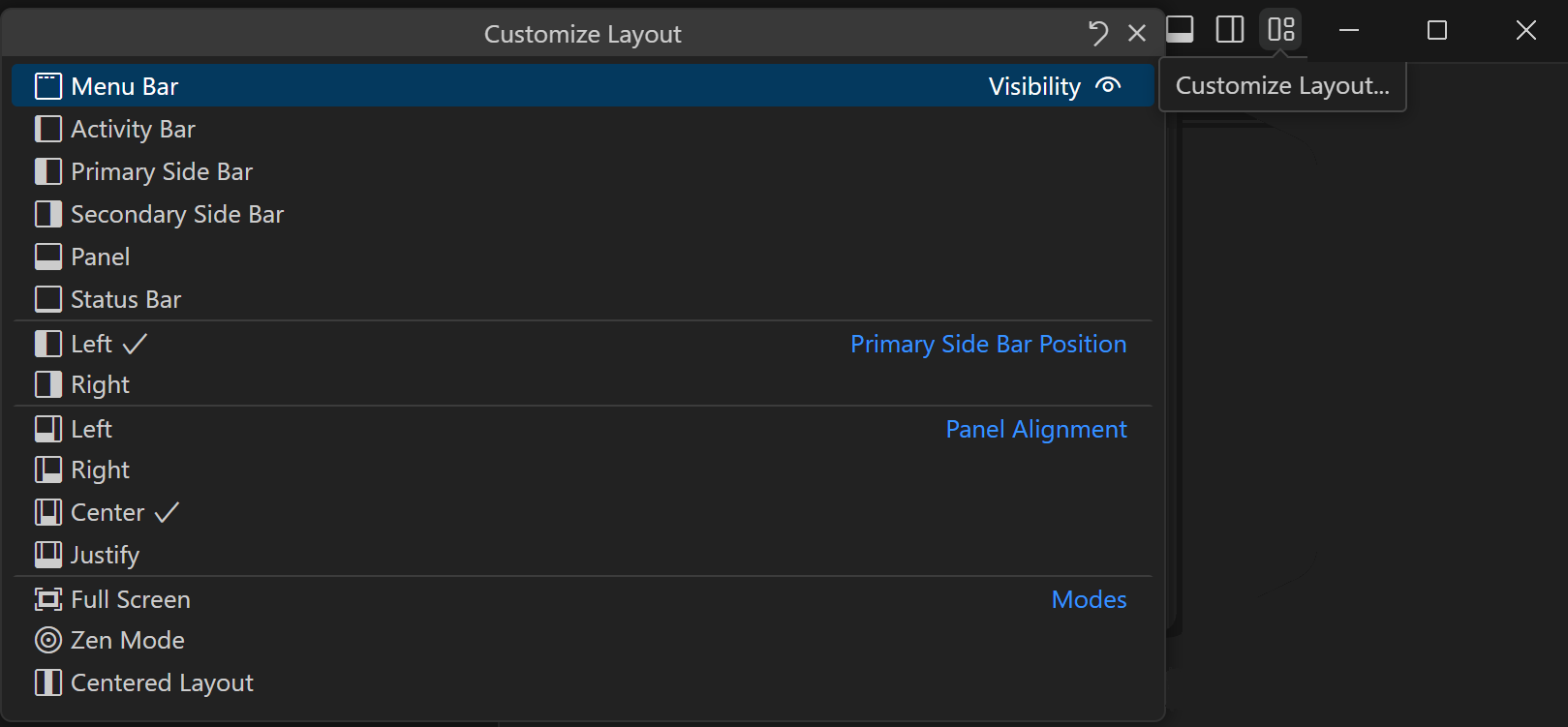
Topics include:
- Primary and Secondary Side Bars
- Panel position and alignment
- Pinned editor tabs
- Editor group layout
- and more
Notable fixes
- 194812 ToC shows up while doing search while
workbench.settings.settingsSearchTocBehaviorset tohide - 195722 Blank settings editor when having network issues
Thank you
Last but certainly not least, a big Thank You to the contributors of VS Code.
Issue tracking
Contributions to our issue tracking:
Pull requests
Contributions to vscode:
Contributions to vscode-js-debug:
Contributions to language-server-protocol: