pgAdmin is a free and open source management tool for PostgreSQL and derivative relation databases such as EDB Advanced Server. It can be installed on multiple OS platforms such as Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, and Windows to manager PostgreSQL 9.2 and above.
Deployment Mode
Contents
pgAdmin can be run as a web or desktop application.
Server Deployment
In server deployment (web application), it is deployed as a web application behind a web server running as a reverse proxy or using the WSGI interface.
Desktop Deployment
In desktop deployment (desktop application), it is deployed to run in desktop mode by utilizing the desktop runtime to host the application. When the runtime is launched from system-tray, it runs the pgAdmin server and launches a web browser to render the user interface.
In this guide, we will install pgAdmin 4 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 & Fedora 29 / Fedora 28 as a web application (server deployment).
Prerequisites
Install PostgreSQL Server
This post assumes that you already have PostgreSQL 9.2 and above installed on your system. Otherwise, follow the post: How To Install PostgreSQL 11 / 10 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7.
Set up EPEL Repository
We would need to enable the EPEL repository to download dependent packages for pgAdmin.
yum install https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
Set up PostgreSQL Repository
pgAdmin 4 is available in PostgreSQL repository and your system should have the PostgreSQL repository by now if you have already completed the installation of PostgreSQL. If not, add the PostgreSQL repository using the below command.
### PostgreSQL 11 ### # RHEL 7 # yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/11/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat11-11-2.noarch.rpm # CentoS 7 # yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/11/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-centos11-11-2.noarch.rpm # Fedora 29 # dnf install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/11/fedora/fedora-29-x86_64/pgdg-fedora11-11-2.noarch.rpm # Fedora 28 # dnf install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/11/fedora/fedora-28-x86_64/pgdg-fedora11-11-2.noarch.rpm ### PostgreSQL 10 ## # RHEL 7 # yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/10/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat10-10-2.noarch.rpm # CentoS 7 # yum install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/10/redhat/rhel-7-x86_64/pgdg-centos10-10-2.noarch.rpm # Fedora 29 # dnf install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/10/fedora/fedora-29-x86_64/pgdg-fedora10-10-4.noarch.rpm # Fedora 28 # dnf install https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/10/fedora/fedora-28-x86_64/pgdg-fedora10-10-4.noarch.rpm
Install pgAdmin 4
Once you have PostgreSQL repository configured on your system, run the following command to install pgAdmin 4.
### RHEL / CentOS ### yum -y install pgadmin4 ### Fedora ### dnf -y install pgadmin4
Start and enable httpd service.
systemctl start httpd systemctl enable httpd
Configure pgAdmin 4
We would need to do a few configuration changes prior to accessing the pgAdmin 4.
Copy the pgAdmin 4 sample configuration.
cp /etc/httpd/conf.d/pgadmin4.conf.sample /etc/httpd/conf.d/pgadmin4.conf
Create a pgAdmin log and data directories.
mkdir /var/log/pgadmin4/ mkdir /var/lib/pgadmin4/
Create/Edit config_local.py file.
vi /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/config_local.py
Add the following settings.
ADVERTISEMENT
LOG_FILE = '/var/log/pgadmin4/pgadmin4.log' SQLITE_PATH = '/var/lib/pgadmin4/pgadmin4.db' SESSION_DB_PATH = '/var/lib/pgadmin4/sessions' STORAGE_DIR = '/var/lib/pgadmin4/storage'
Change permissions of directories so that Apache can write data into it.
chown -R apache:apache /var/lib/pgadmin4/* chown -R apache:apache /var/log/pgadmin4/*
Run the following command to create a user account for the pgAdmin 4 web interface.
python /usr/lib/python2.7/site-packages/pgadmin4-web/setup.py
Output:
NOTE: Configuring authentication for SERVER mode. Enter the email address and password to use for the initial pgAdmin user account: Email address: admin@itzgeek.local Password: xxxxxxxxx Retype password: xxxxxxxxx pgAdmin 4 - Application Initialisation ======================================
Restart the Apache web service.
systemctl restart httpd
Firewall
Set up the firewall so that we can access pgAdmin 4 from external machines.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http firewall-cmd --reload
SELinux
Consider disabling SELinux permanently for pgAdmin 4 to work properly.
Access pgAdmin 4
Open a web browser and go to the following URL to access the pgAdmin 4 interface.
http://ip.add.re.ss/pgadmin4
Log in to pgAdmin 4 web interface using the email address and password you have created earlier.
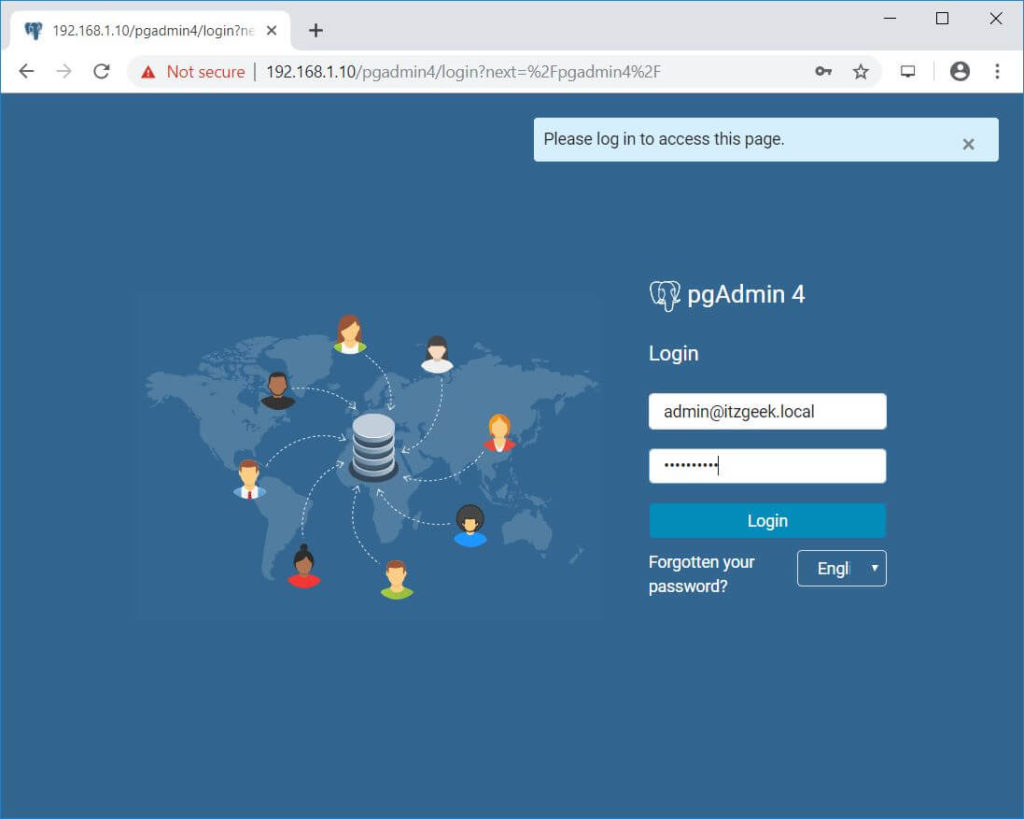
Upon successful login, you should see the pgAdmin 4 interface.
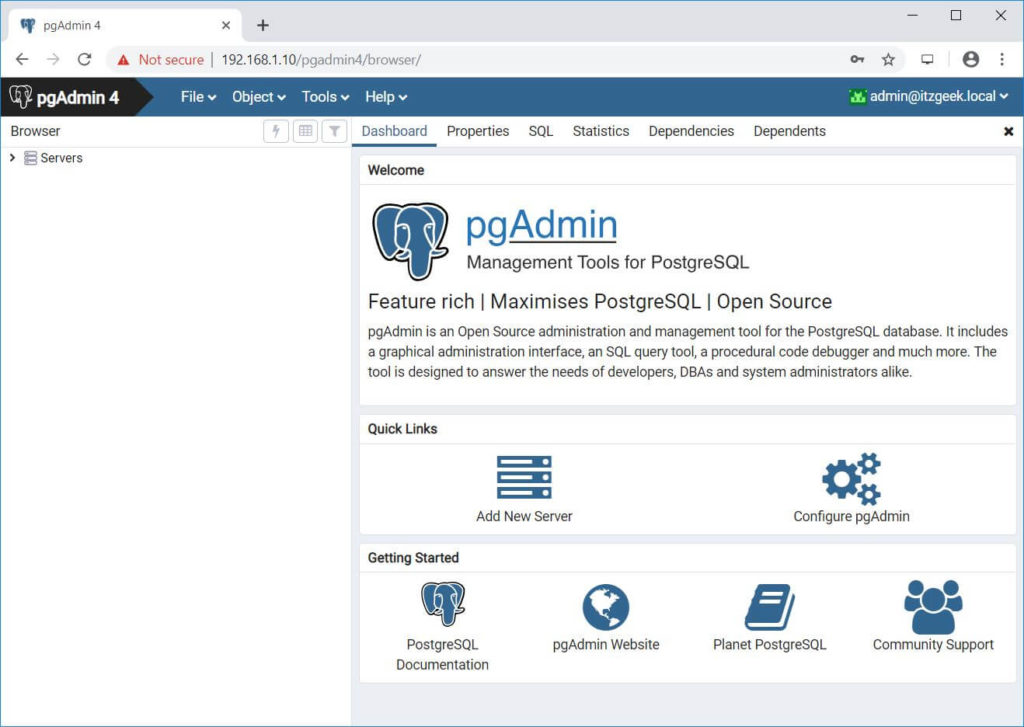
To manage a PostgreSQL server, you will need to add a new server. Click on Add New Server.
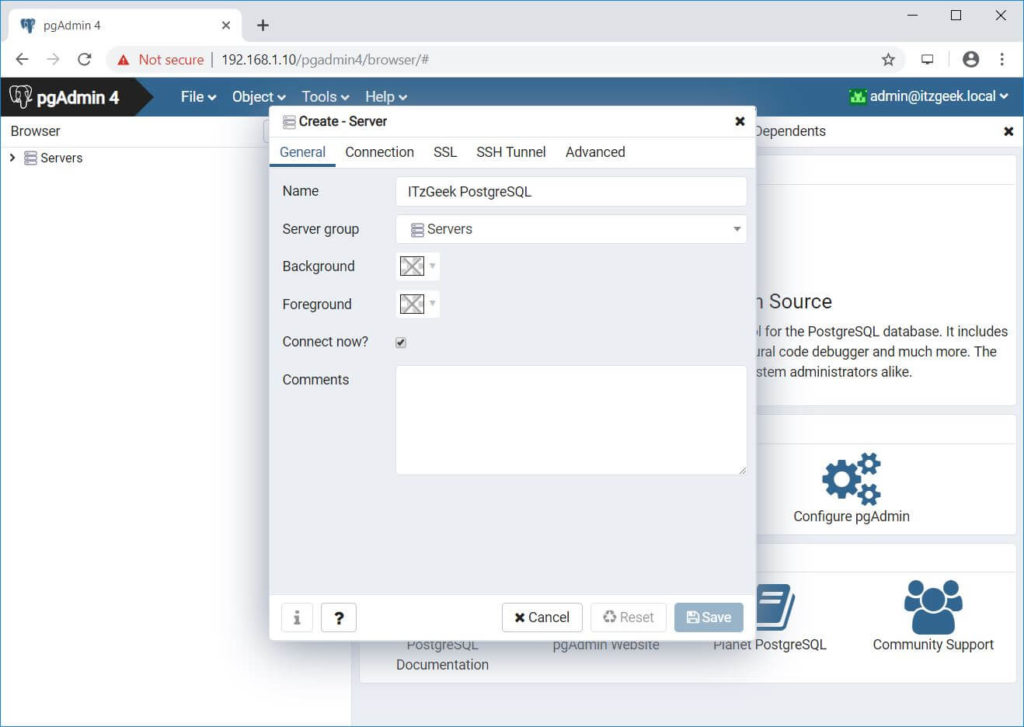
General Tab:
Name:- Name your PostgreSQL Server
Connection Tab:
Hostname/address:- Hostname or IP Address of PostgreSQL server
Port:- 5432 (Leave default) – Change it if required
Username:- Username by which you are connecting. In my case, it is postgres.
Password:- Password for the user
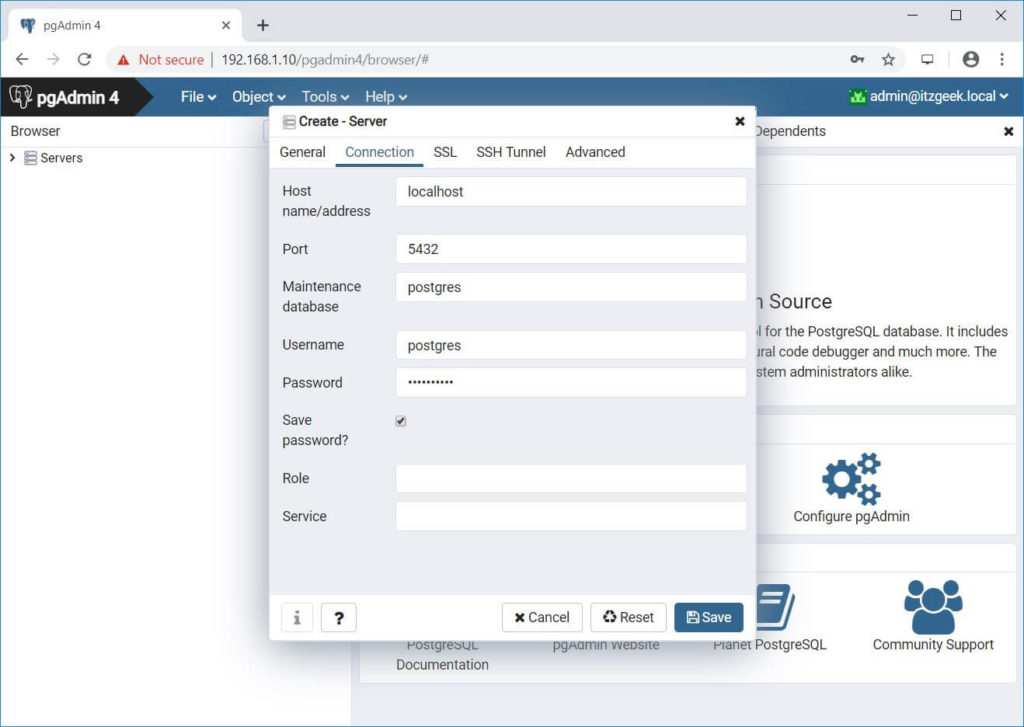
Click Save to save the changes.
ADVERTISEMENT
If the connection to PostgreSQL server is successful, you should see the following page.
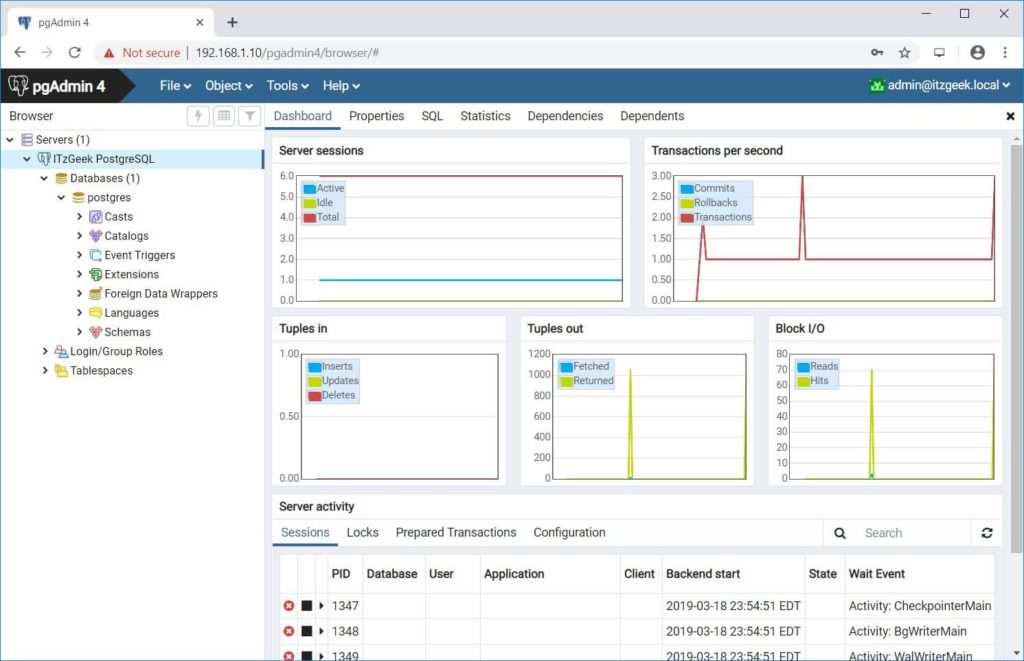
Troubleshooting
You may get a Fatal: Ident authentication failed for user error.
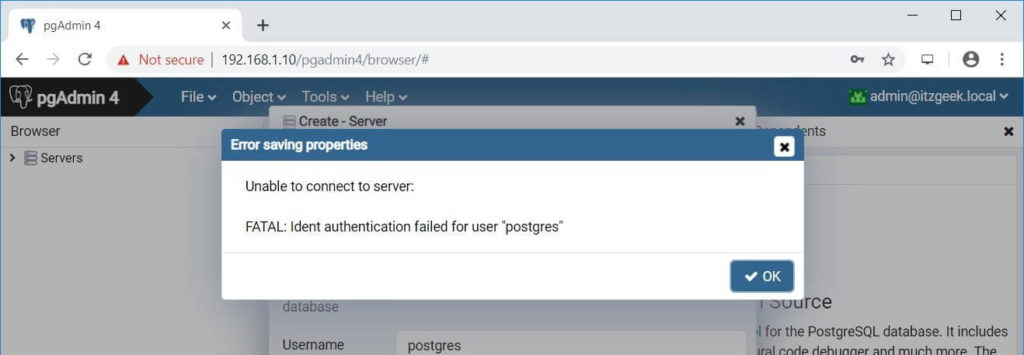
To fix the issue, edit pg_hba.conf file.
### PostgreSQL 11 ### vi /var/lib/pgsql/11/data/pg_hba.conf ### PostgreSQL 10 ### vi /var/lib/pgsql/11/data/pg_hba.conf
Update the below line shown like below.
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD host all all all md5
Restart the PostgreSQL service.
### PostgreSQL 11 ### systemctl restart postgresql-11 ### PostgreSQL 10 ### systemctl restart postgresql-10
Conclusion
You have successfully installed pgAdmin 4 on CentOS 7 / RHEL 7 & Fedora 29 / Fedora 28 and added one of your PostgreSQL instances to it to manage the database. pgAdmin 4 is similar to phpPgAdmin in terms of managing PostgreSQL databases. You can visit pgAdmin 4 documentation for more information.