“We have nothing to fear but …”. famous words of Chief Vitalstatistix , chief of the famous Gaulish village in the famous Asterix & Obelix series.

Legend goes when the Gallic chieftains were asked by Alexander the Great what they were most afraid of in all the world, they replied that their worst fear was that the “sky might fall on their heads”.
In today’s world, the “sky” aka Cloud is the platform for bursting and sustaining application workloads with Cloud service providers offering network services, infrastructure, or business applications in the cloud, thereby helping with kicking off new projects or helping meet business needs for temporary, seasonal, or unplanned demand.
VMware vSphere
Contents
VMware vSphere, the industry leading virtualization platform, provides a powerful, flexible, and secure foundation for business agility that accelerates the digital transformation to cloud computing and success in the digital economy.
With vSphere, customers can now run, manage, connect, and secure their applications in a common operating environment, across clouds and devices. vSphere 6.5 features a dramatically simplified experience, comprehensive built-in security, and a universal app platform for running any app.
More information about what’s new in vSphere 6.5 release can be found here
VMware Cloud on AWS
VMware Cloud on AWS brings VMware enterprise-class Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) software to the AWS Cloud. It enables customers to run production applications across private, public, and hybrid cloud environments based on VMware vSphere, with optimized access to AWS services. It is delivered, sold, and supported by VMware as an on-demand service.IT teams manage their cloud-based resources with familiar VMware tools—without the difficulties of learning new skills or utilizing new tools.
The VMware Cloud on AWS solution enables customers to have the flexibility to treat their private cloud and public cloud as equal partners and to easily transfer workloads between them—for example, to move applications from Dev / Test to production or burst capacity. Users can leverage the global AWS footprint while getting the benefits of elastically scalable SDDC clusters, a single bill from VMware for its tightly integrated software plus AWS infrastructure, and on-demand or subscription services.
More information on VMware Cloud on AWS can be found here.
VMware Cloud on AWS – Initial Availability Configuration
At initial availability, the VMware Cloud on AWS base cluster configuration contains 2TB of memory and four hosts. Each host is configured with 512GB of memory and contains dual CPU sockets that are populated by a custom-built Intel Xeon Processor E5-2686 v4 CPU package. Each socket contains 18 cores running at 2.3GHz, resulting in a physical cluster core count of 144.
VMware Cloud on AWS uses a single, fixed host configuration; the option to add components to the host configuration is not offered at this time.However, the scale-out model enables expansion to up to 16 hosts, resulting in 576 CPU cores and 8TB of memory
More information on the initial availability configuration can be found here.
Oracle Workload Migration
We can rapidly and easily migrate Application workloads by extending on-premises data centers running VMware SDDC to VMware Cloud on AWS using vSphere vMotion technology and back with
- NO VM conversions
- NO Application refactoring and hence NO Application downtime
- NO Networking changes with L2VPN capability between on-prem SDDC and VMware Cloud on AWS
This is key as some cloud providers require some level of refactoring to achieve the above which is not the case here , thereby saving a lot of time, effort and man-hours to trying to plan migrations between on-prem and the Cloud.
vSphere vMotion
VM’s can be migrated from one host or storage location to another location [hot / live or cold migration ] using vSphere vMotion technology. For example, with vSphere vMotion you can move powered on virtual machines away from a host to perform maintenance, to balance loads, to collocate virtual machines that communicate with each other, to move virtual machines apart to minimize fault domain, to migrate to new server hardware, and so on.
More information about vSphere vMotion can be found here.
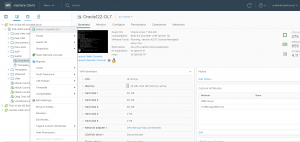
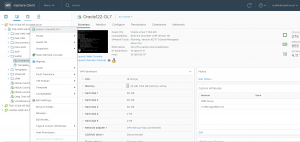
Example of Oracle on prem VMware SDDC Setup
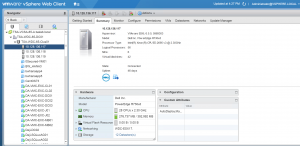
The on-prem setup is shown as below. The Virtual Center ‘TSA-VCSA-65-A.tsalab.local’ manages 3 vSphere servers as shown below.
Each ESXi host has 2 sockets, 14 cores with Hyper Threading with 384 GB memory.
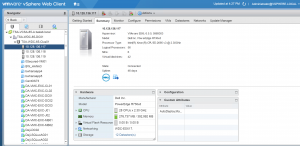
The Storage attached to the ESXI servers is a Tintri VMstore array.
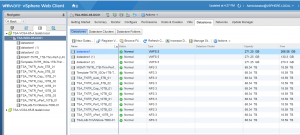
VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ storage is located on the Tintri datastore ‘TSA_TNTR_Perf_10TB_02’.
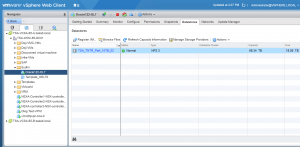
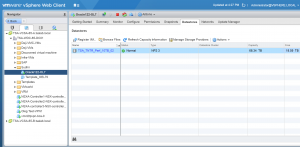
VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ is connected to the distributed port group ‘DPortGroup-10g’ for networking and is assigned an IP 10.128.137.71.
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 network-scripts]# ifconfig -a
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.128.137.71 netmask 255.255.252.0 broadcast 10.128.139.255
ether 00:50:56:8d:c4:52 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 5161998 bytes 314117468 (299.5 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 230 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 14821 bytes 1560090 (1.4 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
loop txqueuelen 0 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 347250 bytes 49099992 (46.8 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 347250 bytes 49099992 (46.8 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 network-scripts]#
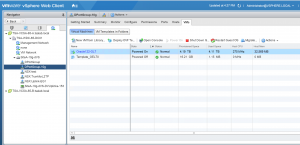
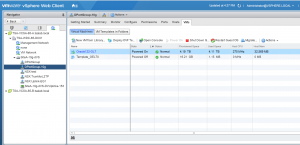
VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ has 16 vCPU’s and 32GB of memory. Oracle SGA is set to 8 GB and PGA set to 2 GB.
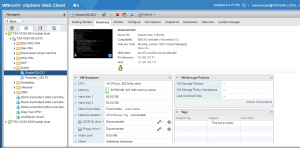
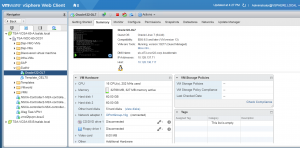
VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ has 3 vmdk’s
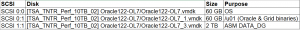
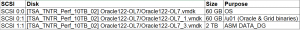
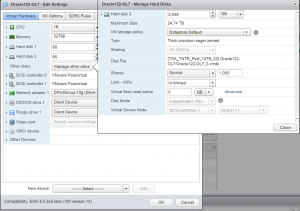
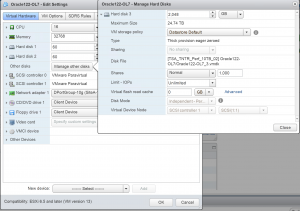
VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ is running OEL 7.4 operating system with Oracle 12.2.0.1.0 Grid Infrastructure and RDBMS binaries. Oracle ASM disks are created using Oracle 12.2 ASM Filter driver (ASMFD).
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 ~]# /u01/app/12.2.0/grid/bin/asmcmd afd_state
ASMCMD-9526: The AFD state is ‘LOADED’ and filtering is ‘ENABLED’ on host ‘sb-ol73-ora122.corp.localdomain’
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 ~]#
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 ~]# /u01/app/12.2.0/grid/bin/asmcmd afd_lsdsk
——————————————————————————–
Label Filtering Path
===========================================
DATA_DISK02 ENABLED /dev/sdc1
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 ~]#
A database ‘ORA12C’ is created on this VM with multi-tenant option running a pluggable database ‘pdb1’. The database is open and running on this VM.
oracle@sb-ol73-ora122:ORA12C:/home/oracle> sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 12.2.0.1.0 Production on Mon Mar 26 10:37:43 2018
Copyright (c) 1982, 2016, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 12c Enterprise Edition Release 12.2.0.1.0 – 64bit Production
SQL> select con_id, DBID,NAME from v$pdbs;
CON_ID DBID NAME
———- ———- ———————-
2 2436379516 PDB$SEED
3 2711234728 PDB1
SQL>
VMware Cloud on AWS setup
The VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC cluster setup is a basic initial availability cluster as shown below.
The setup below shows 4 hosts, each with 2 sockets with 18 cores with Hyper Threading along with 2TB of memory.
VMware creates and operates a separate resource pool to manage customer workloads. Customers have the option to create child resource pools but cannot configure cluster affinity rules at initial availability.
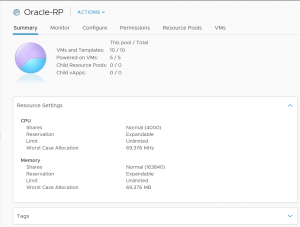
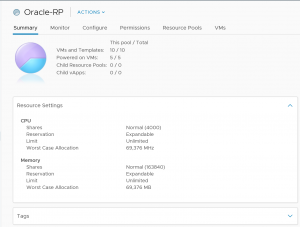
The VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC cluster includes a vSAN all-flash array. At initial availability of VMware Cloud on AWS, each host is equipped with eight NVMe devices and a total of 10TB of raw capacity, not including the cache capacity of the vSAN datastore, for the VMs to consume.
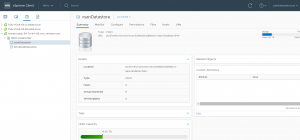
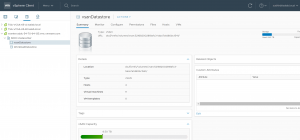
All VMs running inside the cloud SDDC consume storage capacity and leverage storage services from the vSAN datastore. The cloud SDDC introduces a new vSAN capability that provides two logical datastores instead of one. One of these datastores is used to store the management VMs; the other datastore is used for the customer VMs.
More information can be found here.
Layer 2 VPN
Layer 2 VPN (L2VPN) has been established between the on prem VMware SDDC cluster and the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC.
This gives us the capability of vMotioning VM from on-premise to the VMware Cloud on AWS without changing ANY networking aspects (like IP address , Gateway etc) thus making the migration very seamless.
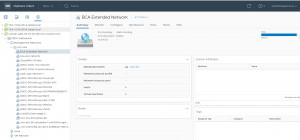
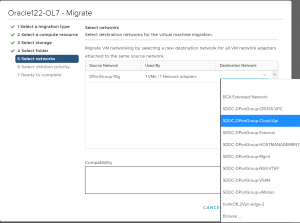
‘BCA Extended Network’ port group needs to assigned as the Destination network port group during the course of specifying the destination network as part of the vMotion operation.
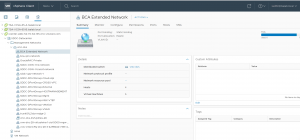
Migrating Oracle Workloads to VMware Cloud on AWS
The goal of this exercise is to see if we can effectively migrate , without any downtime with no changes or application or VM refactoring , with no changes to the networking , the VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ running on prem to the SDDC cluster on VMware Cloud on AWS.
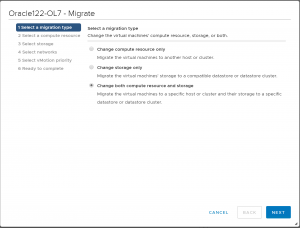
Right Click on the VM, click ‘Migrate’.
Select the ‘Compute and Storage’ migration method
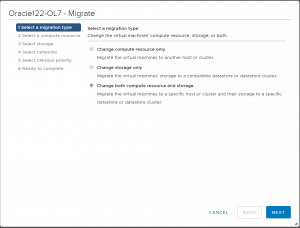
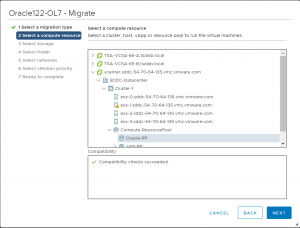
Select the ‘Oracle-RP’ Compute Resource Pool.
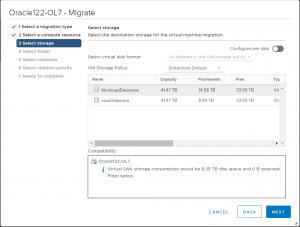
Select the ‘WorkloadDatastore’ datastore for storage.
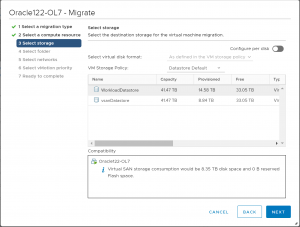
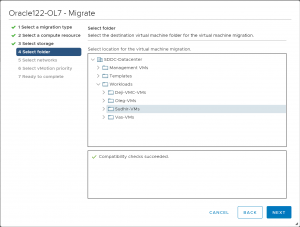
Select appropriate destination folder for VM.
Pick the ‘BCA Extended Network’ as the Destination network Port group.
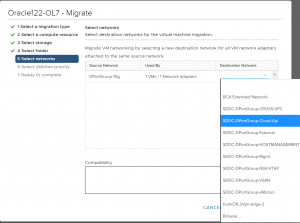
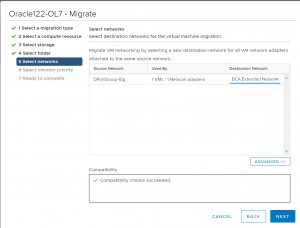
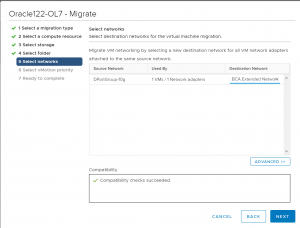
Select the appropriate vMotion priority.
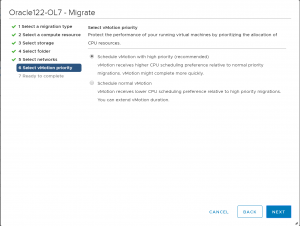
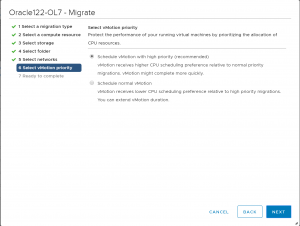
Review the migration and click Finish when ready
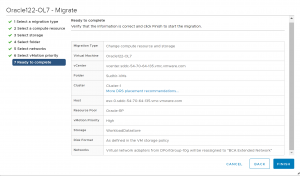
The vMotion operation begins.
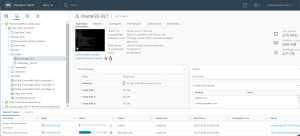
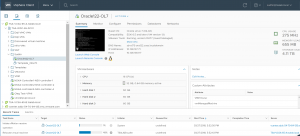
Check the database alert log file for any failures , no failures to report.
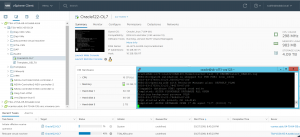
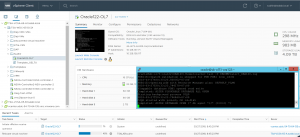
VM ‘Oracle122-OL7’ has been successfully migrated to the VMware Cloud on AWS SDDC.
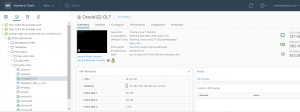
Check the VM network connectivity.
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 network-scripts]# ifconfig -a
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.128.137.71 netmask 255.255.252.0 broadcast 10.128.139.255
ether 00:50:56:8d:c4:52 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 5161998 bytes 314117468 (299.5 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 230 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 14821 bytes 1560090 (1.4 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
loop txqueuelen 0 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 347250 bytes 49099992 (46.8 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 347250 bytes 49099992 (46.8 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 network-scripts]#
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 network-scripts]# ping www.google.com
PING www.google.com (74.125.197.104) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 74.125.197.104 (74.125.197.104): icmp_seq=1 ttl=38 time=95.8 ms
64 bytes from 74.125.197.104 (74.125.197.104): icmp_seq=2 ttl=38 time=95.4 ms
64 bytes from 74.125.197.104 (74.125.197.104): icmp_seq=3 ttl=38 time=95.2 ms
64 bytes from 74.125.197.104 (74.125.197.104): icmp_seq=4 ttl=38 time=96.9 ms
64 bytes from 74.125.197.104 (74.125.197.104): icmp_seq=5 ttl=38 time=94.4 ms
^C
— www.google.com ping statistics —
5 packets transmitted, 5 received, 0% packet loss, time 4006ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 94.406/95.566/96.913/0.836 ms
[root@sb-ol73-ora122 network-scripts]#
Demo
A video of the above steps can be found here.
Conclusion
VMware Cloud on AWS brings VMware enterprise-class Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC) software to the AWS Cloud. It enables customers to run production applications across private, public, and hybrid cloud environments based on VMware vSphere, with optimized access to AWS services. The VMware Cloud on AWS solution enables customers to have the flexibility to treat their private cloud and public cloud as equal partners and to easily transfer workloads between them—for example, to move applications from Dev / Test to production or burst capacity.
We can rapidly and easily migrate Application workloads by extending on-premises data centers running VMware SDDC to VMware Cloud on AWS using vSphere vMotion technology and back with
- NO VM conversions
- NO Application refactoring and hence NO Application downtime
- NO Networking changes with L2VPN capability between on-prem SDDC and VMware Cloud on AWS
All Oracle on VMware SDDC collaterals can be found at the post ‘Oracle on VMware Collateral – One Stop Shop‘.
More information on VMware Cloud on AWS can be found at the post.