Seeing the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG message in Firefox?
This error usually means your browser or server isn’t handling HTTPS traffic correctly – often due to a simple configuration issue.
This guide explains what causes the error and how to fix it, whether you’re a site visitor or a server administrator.
What the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG Error Means
Contents
- 1 What the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG Error Means
- 2 How to Fix the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG Error
- 3 How Developers and Admins Can Fix the Error
- 3.1 Use an Online SSL/TLS Diagnostic Tool
- 3.2 Verify Your Server’s Port and Protocol Configuration
- 3.3 Verify Port and Protocol Settings
- 3.4 Check Certificate Installation
- 3.5 Update TLS and Cipher Settings
- 3.6 Audit the SSL Certificate Installation and Validity
- 3.7 Update and Strengthen Your TLS Version and Cipher Suites
- 4 Simplifying SSL Management with RunCloud
- 5 Final Thoughts: Simplify SSL Management
- 6 FAQs
- 6.1 What causes the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error in Firefox?
- 6.2 Is the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error my fault or the website’s?
- 6.3 Why does the website work in other browsers but not in Firefox?
- 6.4 How can I fix the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error as a website visitor?
- 6.5 As a developer, what is the most common fix for this error?
- 6.6 Is it safe to bypass this error by changing my browser’s security settings?
- 6.7 How can RunCloud help prevent this error?
When you use Firefox to browse the web, you might occasionally see the error message “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG”. While the name sounds complicated, the reason behind it is usually quite simple.
Firefox shows this error when it tries to load a secure (HTTPS) page but receives an unencrypted or invalid response instead. In most cases, the site’s SSL configuration is incorrect, or it’s using outdated security protocols.
This error can be caused by multiple issues. Let’s break down the common causes:
Common Server-Side Causes of the Error
In most situations, the problem isn’t with your computer or browser but with how the website you’re trying to visit is set up.
- Incorrect port configuration: Firefox connects to HTTPS sites through port 443. If the server handles plain HTTP traffic on this port, Firefox will stop the connection and show this error.
- Outdated security protocols: Servers still using old SSL or TLS versions (1.0 or 1.1) can’t complete the handshake with modern browsers.
- Certificate problems: Expired, misconfigured, or mismatched certificates prevent Firefox from validating the site’s identity.
Common Browser or Client-Side Causes
Although it is less common, this error can also be caused by the settings on your own computer or within Firefox.
- Cached data: Outdated cookies or cache files can confuse Firefox when a site’s security settings change.
- Proxy settings: Incorrect proxy configuration (especially on corporate networks) can block HTTPS connections.
- Extensions: Overactive security or ad-blocker add-ons may interfere with the TLS handshake.
Suggesed read: How to Fix err_ssl_protocol Error
How to Fix the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG Error
We now know what causes the SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG error. Let’s see how to fix this quickly and easily:
Clear Your Browser’s Cookies and Cache
As we explained above, sometimes browsers try to connect using outdated information, which can cause errors. To fix this, we will simply clear and delete all the cookies and cache for that particular site. This forces Firefox to download a fresh, correct copy of the website.
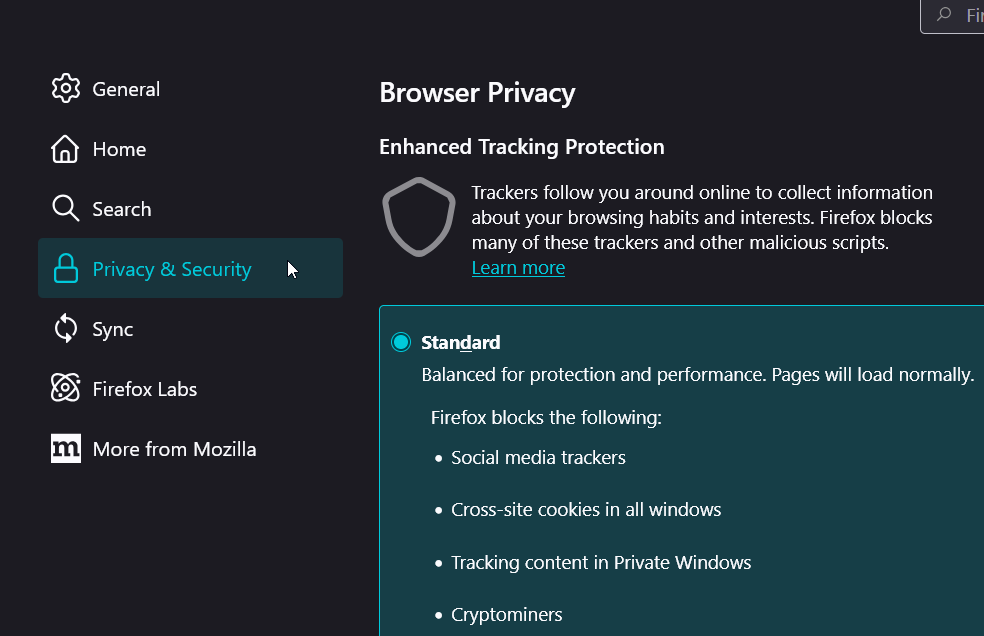
1. Clear cache and cookies: Go to Settings → Privacy & Security → Clear Data, select both checkboxes, and confirm. Then restart Firefox and reload the page.
2. Check proxy settings: Go to Settings → General → Network Settings → Settings…. Choose No proxy, unless you’re on a network that requires one.
3. Disable extensions: Restart Firefox in Troubleshoot Mode. If the site loads, re-enable your add-ons one at a time to find the culprit.
4. Update Firefox: Go to Help → About Firefox to install the latest version.
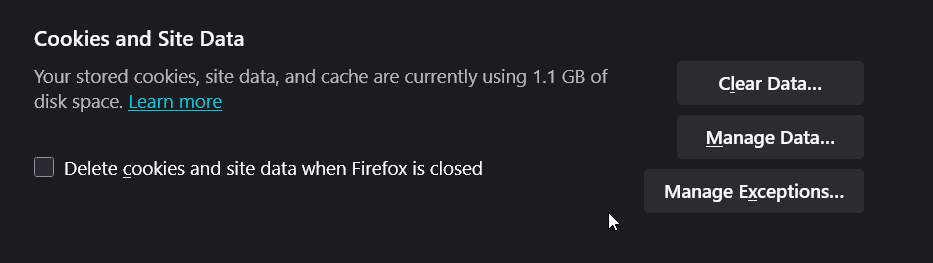
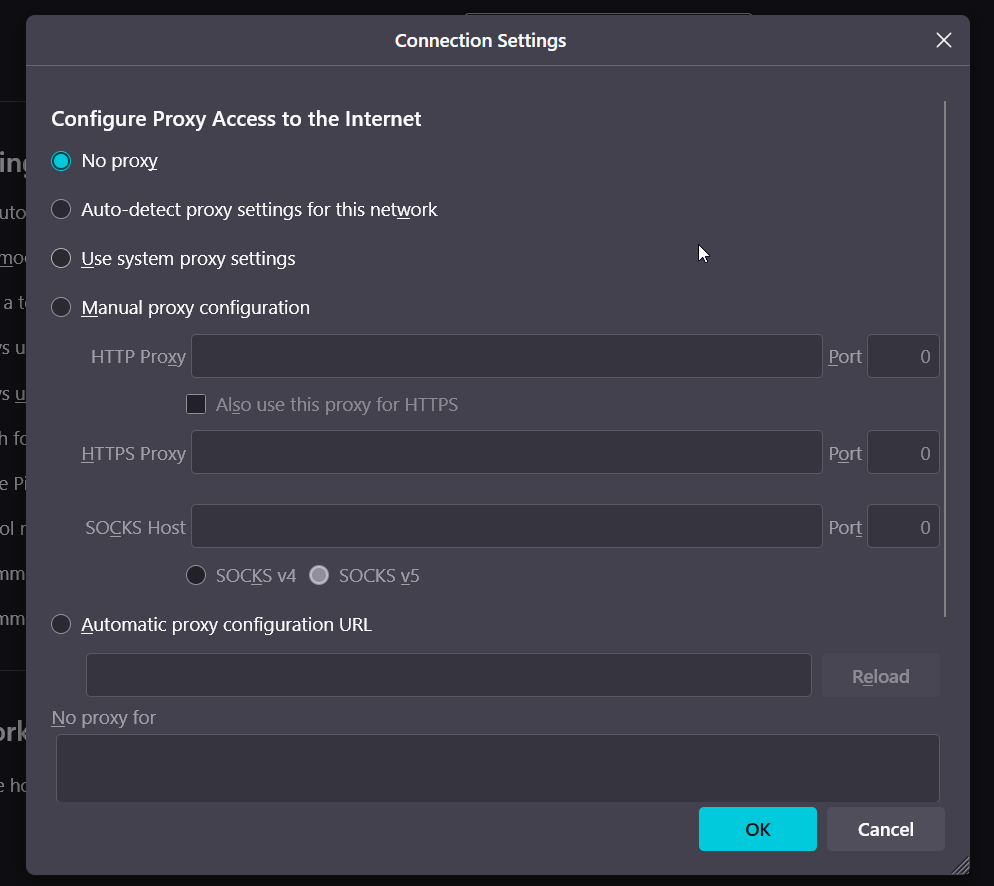
Check Your Proxy Settings
Most home internet users connect directly to the web. However, some users on a company or school network use a “proxy server”. This proxy server intercepts all the traffic coming into the network, which can cause errors on the site. If you are using a proxy server, make sure it is configured correctly on your computer:
- Go to the Settings menu again (click the three lines in the top-right).
- On the General tab, scroll to the bottom to “Network Settings” and click the Settings… button.
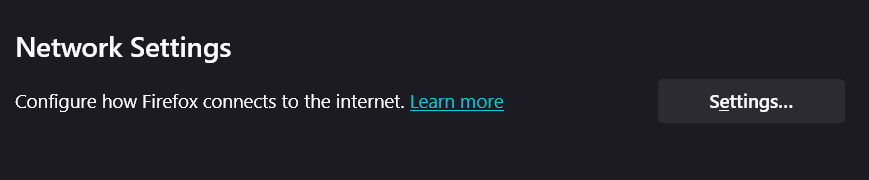
- This will open a new window. The correct setting for most home users is “No proxy“. If it’s set to something else, change it to “No proxy” and click OK.
Note: If you are on a corporate or school network, you may need a proxy. If changing this setting breaks your internet connection, revert it and check with your IT department.
Temporarily Disable Your Browser Add-ons
As we discussed above, some browser extensions interfere with network connections, and you can fix this by simply disabling the problematic extension.
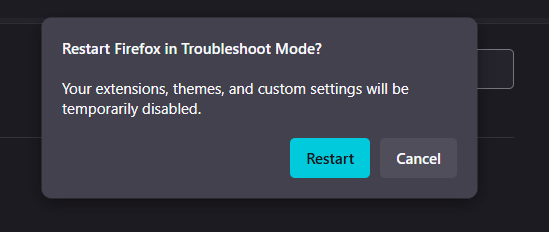
- The fastest way to do this is by restarting Firefox in Troubleshoot Mode (previously called Safe Mode). This temporarily disables all your add-ons.
- Click the three-line menu, go to Help, and then select Troubleshoot Mode….
- Click Restart.
Once Firefox restarts, try visiting the website again. If it works now, you know an add-on is the problem! You can then follow the steps below to find out which one.
- Go to the menu and select Add-ons and Themes (or press Ctrl+Shift+A).
- Click on Extensions.
- Disable your extensions one by one using the blue toggle switch, reloading the problem website after each one. When the site finally loads correctly, you’ll find the extension causing the issue.
Update Your Browser
The world of internet security is constantly evolving. Every few years, new security protocols (the “rules” for the handshake) are released, and old ones are retired. An outdated browser might not know the latest, most secure handshake that modern websites use to communicate on the Internet. Making sure Firefox is up-to-date ensures it has all the modern tools it needs to connect securely.
- Click the three-line menu and go to Help.
- Select About Firefox.
- A small window will pop up and automatically check for updates. If an update is available, it will download and install it for you.

If none of the browser fixes worked, the issue is almost certainly on the server. Here’s how to diagnose and correct it as a developer.
How Developers and Admins Can Fix the Error
If you are a website administrator, then you are in the best position to resolve the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error for your website. This error is almost always a sign of a server-side misconfiguration, where the server sends an unexpected response during the initial TLS handshake. The following detailed checks will help you diagnose and fix the underlying issue.
Use an Online SSL/TLS Diagnostic Tool
Before you spend too much time manually combing through configuration files, you should use an external tool to give you a detailed report. These services test your server from the perspective of an external client and can pinpoint subtle misconfigurations that are easy to miss.
You can use a service like Qualys SSL Labs’ SSL Test or DigiCert SSL Installation Diagnostics Tool to perform a deep analysis of your entire SSL/TLS setup. It will grade your configuration and provide a detailed report on protocol support, key exchange, cipher strength, and certificate chain issues.
The report will explicitly flag common problems such as an incomplete certificate chain (“Chain issues: Incomplete”), support for insecure protocols, or weak cipher suites. This provides an actionable checklist of items to fix within your server’s configuration files.
Verify Your Server’s Port and Protocol Configuration
This is the most frequent cause of the error.
Verify Port and Protocol Settings
- NGINX: Add listen 443 ssl; to your configuration block.
- Apache: Use <VirtualHost _default_:443> and ensure SSLEngine on is enabled with valid certificate file paths.
Check Certificate Installation
- Install both your main certificate and the intermediate chain from your CA.
- Confirm the certificate’s CN or SAN matches your domain.
- Renew any expired certificates.
Update TLS and Cipher Settings
- Enable TLS 1.2 and 1.3 only.
- Disable older protocols (TLS 1.0, 1.1, SSLv2, SSLv3).
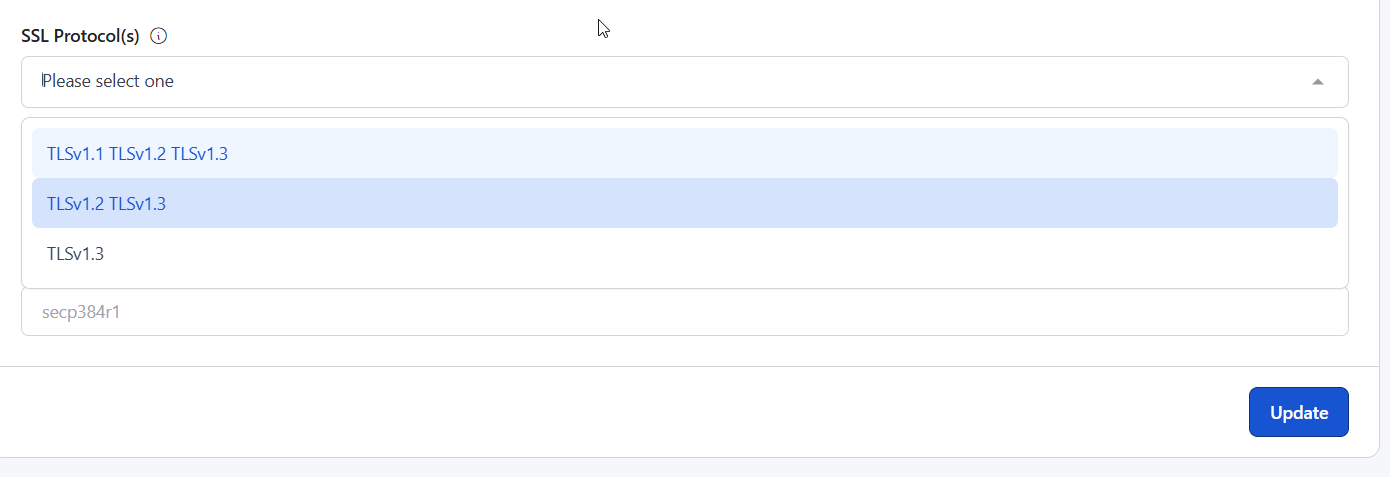
- In RunCloud, select your preferred TLS version from the dropdown menu in the TLS settings.
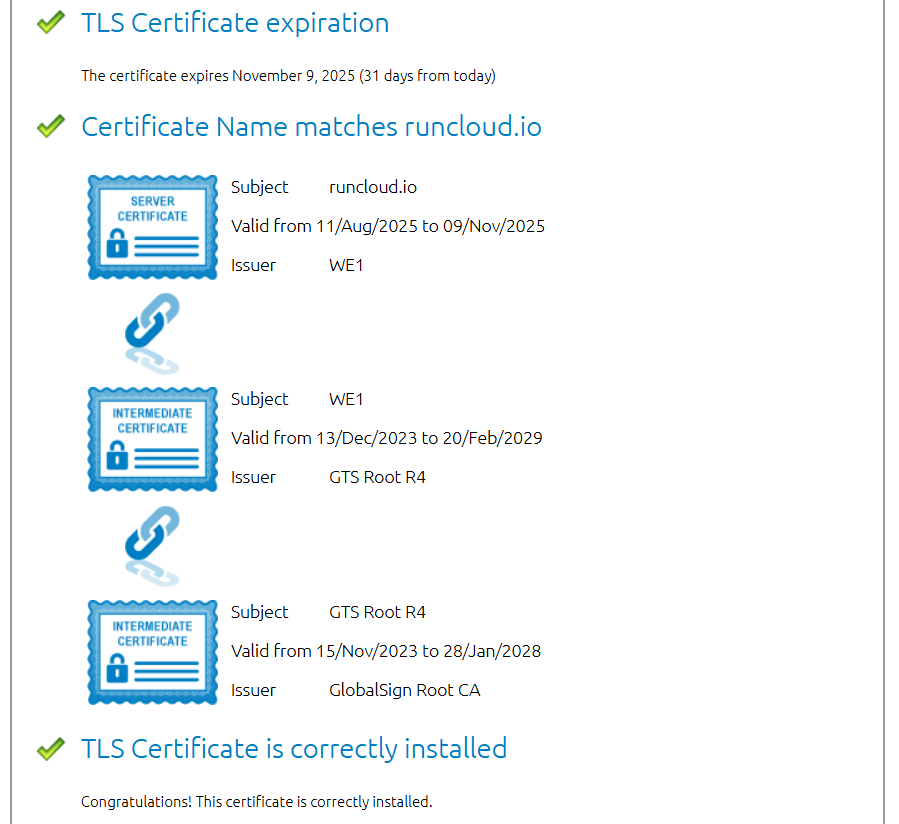
Audit the SSL Certificate Installation and Validity
A faulty SSL certificate setup can prevent the TLS handshake from even beginning properly. The browser needs to validate a complete and correct certificate “chain of trust” to proceed. Any break in this chain or mismatch in information will cause connection failures.
- Check for Correct Installation: Ensure that you have installed not just the primary domain certificate but also the necessary intermediate certificates provided by your Certificate Authority (CA). A missing intermediate certificate breaks the chain of trust, and while some browsers can fetch them, it is not reliable behavior.
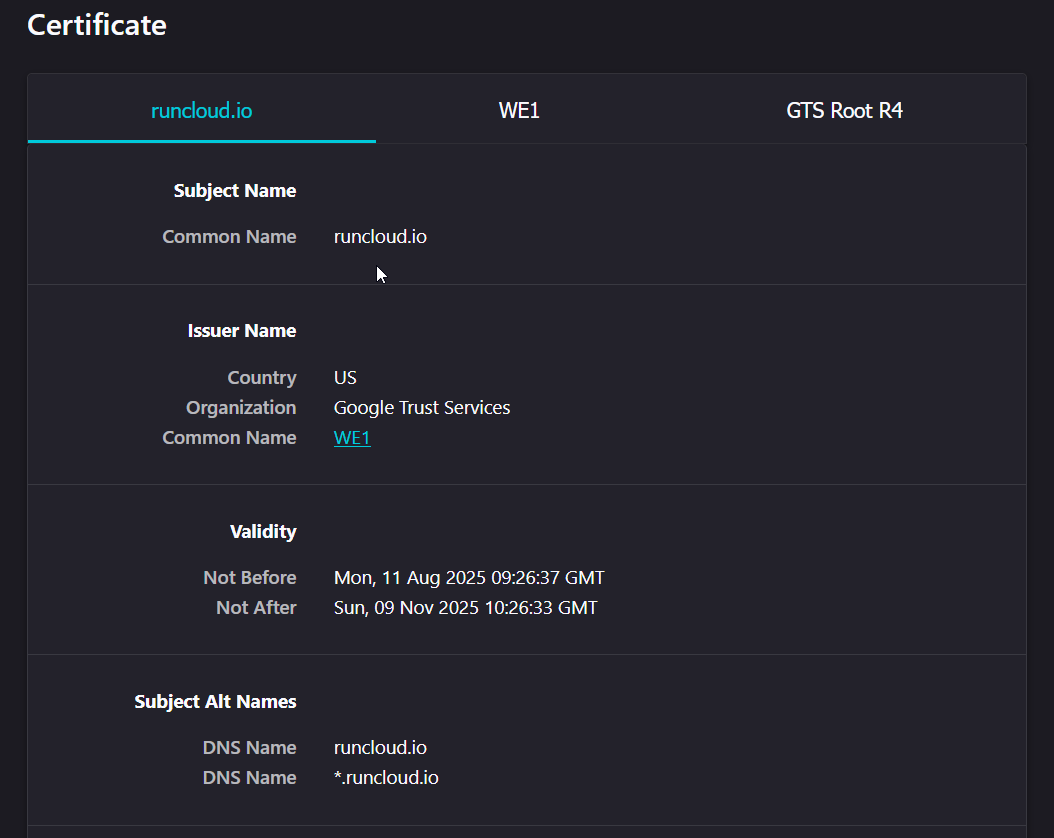
- Verify Domain Name Matching: The certificate’s Common Name (CN) or, more modernly, a name in the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) field must exactly match the domain the user is accessing. A certificate issued for www.example.com will not be valid for example.com unless both are listed in the SAN.
- Confirm Expiration: While usually leading to a different error, an expired certificate can sometimes contribute to configuration issues that manifest as this error. Always confirm your certificate is within its validity period.
Update and Strengthen Your TLS Version and Cipher Suites
Modern browsers, including Firefox, have deprecated older, insecure versions of the TLS protocol (specifically TLS 1.0 and 1.1). If your server is configured only to support these outdated versions, Firefox will refuse to connect, which can sometimes result in this specific error. You must ensure your server is configured to negotiate a modern, secure protocol.
- Enable Modern Protocols: Your server configuration should be set to enable TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3, the current industry standards for security.
- Disable Obsolete Protocols: Explicitly disable support for TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, and all versions of SSL (SSLv2, SSLv3). This not only resolves compatibility issues but is also the best security practice to protect against known vulnerabilities.
If you are using RunCloud, you can do this very easily by selecting the right value from a dropdown menu in your TLS certificate settings.
Simplifying SSL Management with RunCloud
Configuring SSL manually can be slow and error-prone.
RunCloud simplifies it with one-click SSL setup, automatic renewals, and a staging environment for safe testing, helping you avoid common issues like this Firefox error.
One-Click SSL Certificates with Auto-Renewal
RunCloud offers a seamless integration with Let’s Encrypt, a free and trusted certificate authority. With RunCloud, you can:
- Install SSL with a Single Click: Secure your websites with a valid SSL/TLS certificate in seconds, directly from your RunCloud dashboard.
- Automated Renewals: RunCloud automatically handles the renewal of your Let’s Encrypt certificates, ensuring your sites remain secure without any manual intervention. This eliminates the risk of expired certificates causing errors.
Making changes directly to a live server can be risky and can inadvertently lead to configuration errors. RunCloud’s staging environment provides a safe sandbox to test any modifications before deploying them to your production site.
Once you’ve verified that your changes are working correctly in the staging environment, you can easily sync them with your live site.
Final Thoughts: Simplify SSL Management
Managing SSL manually can take hours – and a single misstep can break your site.
With RunCloud, you can deploy, renew, and manage SSL certificates in seconds through an intuitive dashboard.
Start your free RunCloud trial today and secure your sites the easy way.
FAQs
What causes the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error in Firefox?
This error almost always signals a misconfiguration on the web server. It happens when Firefox expects a secure (HTTPS) response but receives unencrypted data, often because the server isn’t correctly configured to handle SSL/TLS traffic on the proper port (443). Other causes include an improperly installed SSL certificate or the use of outdated and insecure TLS protocols by the server.
Is the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error my fault or the website’s?
In the vast majority of cases, this error originates from the website’s server, not your browser or computer. While clearing your browser’s cache or checking proxy settings can sometimes help, the fundamental problem usually needs to be fixed by the website’s developer or administrator.
Why does the website work in other browsers but not in Firefox?
Firefox is often more stringent and particular about its enforcement of SSL/TLS protocols and security standards. While other browsers might be more lenient with minor server misconfigurations, Firefox’s strict security posture will flag these issues, resulting in the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error. This means the underlying server issue still exists, even if other browsers don’t display an error.
How can I fix the “SSL_ERROR_RX_RECORD_TOO_LONG” error as a website visitor?
As a visitor, your troubleshooting options are limited to your own browser. The most effective steps are to clear your Firefox cache and cookies, disable any proxy settings, and temporarily disable browser extensions to rule out any local conflicts. If the error persists after these steps, the issue must be resolved by the website owner.
As a developer, what is the most common fix for this error?
The most frequent cause and fix for developers is an incorrect port configuration on the web server. You must ensure your server is explicitly configured to listen for secure traffic on port 443 (e.g., listen 443 ssl; in NGINX). Verifying that your SSL certificate is correctly installed and valid and that you are using modern TLS versions (TLS 1.2 or 1.3) will resolve most other instances of this error.
Is it safe to bypass this error by changing my browser’s security settings?
No, it is highly discouraged to lower your browser’s security settings, such as forcing it to accept an outdated TLS version, to bypass this error. Doing so can expose your browsing activity to security vulnerabilities and defeat the purpose of a secure connection. The error is a warning that the site’s security is not properly configured, and the website’s administrator is responsible for the fix.
How can RunCloud help prevent this error?
RunCloud helps prevent this error by simplifying and automating server and SSL management. With features like one-click SSL certificate installation and automatic renewals, RunCloud ensures your certificates are always valid and correctly configured, eliminating a common cause of the error. Furthermore, its easy-to-use dashboard and staging environments allow you to test server changes safely, reducing the risk of misconfigurations that could lead to SSL issues on your live site.