Ruby on Rails® also known as Rails, is an open-source web framework written in Ruby. It helps you create highly powerful web sites and applications.
Rails is released under MIT license and was first released in 2005 by David Heinemeier Hansson.
Here, we will install Ruby on Rails on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8.
Prerequisites
Contents
Before installing Ruby, enable EPEL repository on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 to get dependent packages.
Install the development packages.
dnf install -y git-core zlib zlib-devel gcc-c++ patch readline readline-devel libyaml-devel libffi-devel openssl-devel make bzip2 autoconf automake libtool bison curl sqlite-devel
Install Node.js
We will install Node.js to provide a functionality of CoffeeScript and the Asset Pipeline in Rails, depend on a Javascript runtime.
Here, we will use the Long Term Supported version for our Ruby on Rails installation.
If you want to make use of the latest feature, install Node.js v13.x.
curl -sL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_12.x | bash - dnf install -y nodejs
Validate the Node.js version with the below command.
node -v
Output: v12.16.1
Install Yarn
If you want to install the Yarn package manager, please perform the below steps.
curl -sL https://dl.yarnpkg.com/rpm/yarn.repo | sudo tee /etc/yum.repos.d/yarn.repo dnf install -y yarn
Install Ruby
Using rbenv (Recommended)
The rbenv provides an easy way to install and manage the versions of Ruby, and it is simpler than RVM.
To install rbenv, you have to run these commands.
git clone https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv.git ~/.rbenv
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.rbenv/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
echo 'eval "$(rbenv init -)"' >> ~/.bashrc
exec $SHELL git clone https://github.com/rbenv/ruby-build.git ~/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
exec $SHELL
The above commands will install rbenv into your home directory and would set appropriate environment variables.
Verify that rbenv is correctly setup.
curl -fsSL https://github.com/rbenv/rbenv-installer/raw/master/bin/rbenv-doctor | bash
Output: Checking for `rbenv' in PATH: /home/raj/.rbenv/bin/rbenv Checking for rbenv shims in PATH: OK Checking `rbenv install' support: /home/raj/.rbenv/plugins/ruby-build/bin/rbenv-install (ruby-build 20200224) Counting installed Ruby versions: none There aren't any Ruby versions installed under `/home/raj/.rbenv/versions'. You can install Ruby versions like so: rbenv install 2.2.4 Checking RubyGems settings: OK Auditing installed plugins: OK
We will install the latest version of Ruby (v2.7.0). The installation may take 15 to 20 minutes to complete, so please be patient.
rbenv install 2.7.0
If you want to install or use the different versions of Ruby, run the rbenv install [version] command with a different Ruby version rbenv install -l.
Set Ruby v2.7.0 as the default version for all shells.
rbenv global 2.7.0
Check the Ruby version.
ruby -v
Output: ruby 2.7.0p0 (2019-12-25 revision 647ee6f091) [x86_64-linux]
If you do not want RubyGems to install the documentation, then add the –no-ri and –no-roc in ~/.gemrc file.
echo "gem: --no-ri --no-rdoc" > ~/.gemrc
Install the bundler.
gem install bundler
Using RVM
RVM (Ruby Version Manager) provides an easy way to install and manage ruby versions independently by automatically downloading its dependencies.
Import the public key in your system.
gpg --keyserver hkp://keys.gnupg.net --recv-keys 409B6B1796C275462A1703113804BB82D39DC0E3 7D2BAF1CF37B13E2069D6956105BD0E739499BDB
Use the curl command to install RVM in your system.
curl -sSL https://get.rvm.io | bash -s stable
Load RVM environment variables using the below command.
source /etc/profile.d/rvm.sh
With RVM, you can install and manage multiple Ruby versions on the single system.
Use the below command to install Ruby 2.7.0.
rvm install 2.7.0
You can also install a different version of Ruby using the rvm install [version] command.
Set Ruby v2.7.0 as default in case your system has multiple versions of Ruby.
rvm use 2.7.0 --default
Output: Using /usr/local/rvm/gems/ruby-2.7.0
Check the Ruby version.
ruby -v
Output: ruby 2.7.0p0 (2019-12-25 revision 647ee6f091) [x86_64-linux]
Install the bundler.
gem install bundler
Install Rails
We will install latest version of Rails (v6.0.2.2) with this command. You can also install an older version of Rails by mentioning the version with –v [version] during installation.
gem install rails
Verify the version of Rails.
rails -v
Output: Rails 6.0.2.2
Firewall
By default, Ruby on Rails listens on port 3000. So, we need to allow TCP 3000 in firewall in order to access it from external machines.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=3000/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
Create a Test Application
To ensure our Ruby on Rails installation went smoothly, we will create a test application with MariaDB support to test it out.
Install Database
Rails comes with sqlite3 as the default database, which is not recommended to use in a production environment.
For high traffic web applications, you’ll probably want to go with MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Here, we will install and use MariaDB (v10.3) as a database for our application.
READ: Install MariaDB v10.4 On CentOS 8 / RHEL 8.
In case, you chose to install MariaDB v10.4 from the MariaDB community, you must install MariaDB-devel and MariaDB-shared packages for Rails.
dnf install -y mariadb-server mariadb mariadb-devel systemctl start mariadb systemctl enable mariadb
Run mysql_secure_installation command to secure your MariaDB installation.
Install the mysql2 extension.
gem install mysql2
Create Rails Application
Create a new application in your home directory.
cd ~ rails new itzgeekapp -d mysql cd itzgeekapp
Edit your application’s database configuration config/database.yml file.
vi config/database.yml
Update the database username and password.
default: &default adapter: mysql2 encoding: utf8mb4 pool: %= ENV.fetch("RAILS_MAX_THREADS") { 5 } %> username: root password: password # Replace with MariaDB / MySQL user password socket: /var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock
Create the database.
rake db:create
Output: Created database 'itzgeekapp_development' Created database 'itzgeekapp_test'
Validate Application
Go to the application directory.
cd itzgeekapp
Start your rails application.
rails server -b 0.0.0.0
Output: => Booting Puma
=> Rails 6.0.2.2 application starting in development
=> Run `rails server --help` for more startup options
Puma starting in single mode...
* Version 4.3.3 (ruby 2.7.0-p0), codename: Mysterious Traveller
* Min threads: 5, max threads: 5
* Environment: development
* Listening on tcp://0.0.0.0:3000
Use Ctrl-C to stop
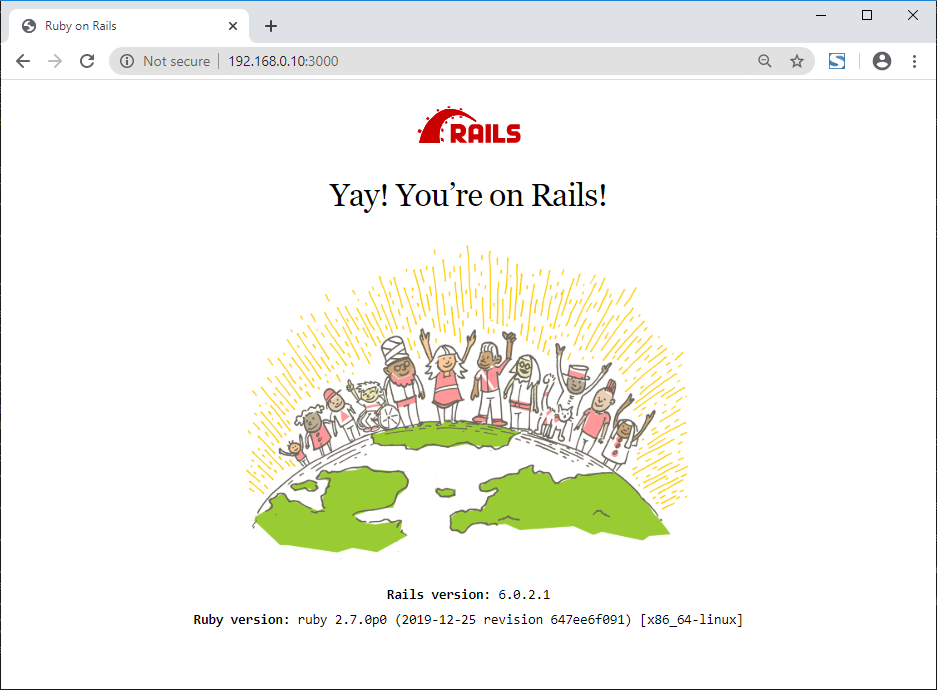
If everything is working properly, your Rails application should be running on port 3000.
Visit your Rails application by typing the below URL in your web browser.
http://localhost:3000
OR
http://your.ip.add.ress:3000
You should get the following page.
Conclusion
That’s All. You have successfully installed on Ruby on Rails on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8. Please share your feedback in the comments section.