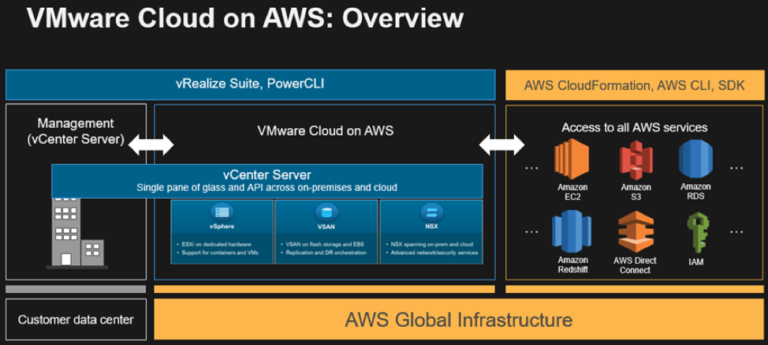
vCloud Director exposes NSX load balancing services through the edge gateways, which enables tenant users to deploy their own load balancer instances. However, this makes sense only for the local site.
In this blog post, we will show you how by integrating F5 Big-IP with vCloud Director, you can have an abstract multi-site load balancer, which uses DNS-based load sharing to distribute the load between the sites using several edge gateways. And we will expose this functionality to the tenant users through an vCloud Director UI extension.
vCloud Director Load Balancing Solution Architecture
Contents
The diagram outlines the solution architecture – a multi-site application and the management of the application load balancing.
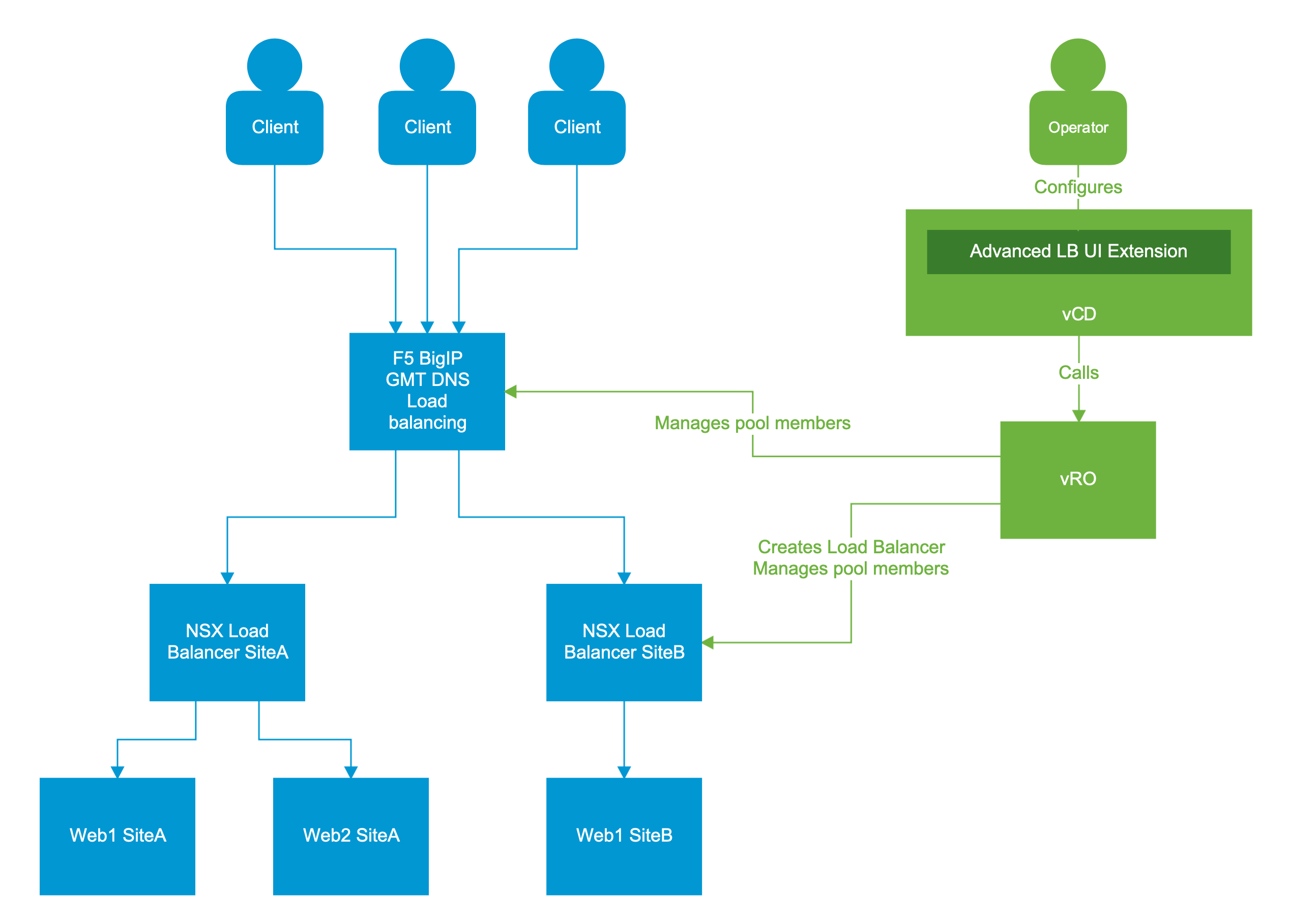
The multi-site application (in blue) runs on two datacenters and has a DNS load balancer, which redirects the application end-user requests to the proper site.
The management of the application load balancing (in green) consists of an Advanced Load Balancing UI extension backed by vRO.
Solution
Let’s see how to set up the advanced load balancing process and what will happen in the backend.
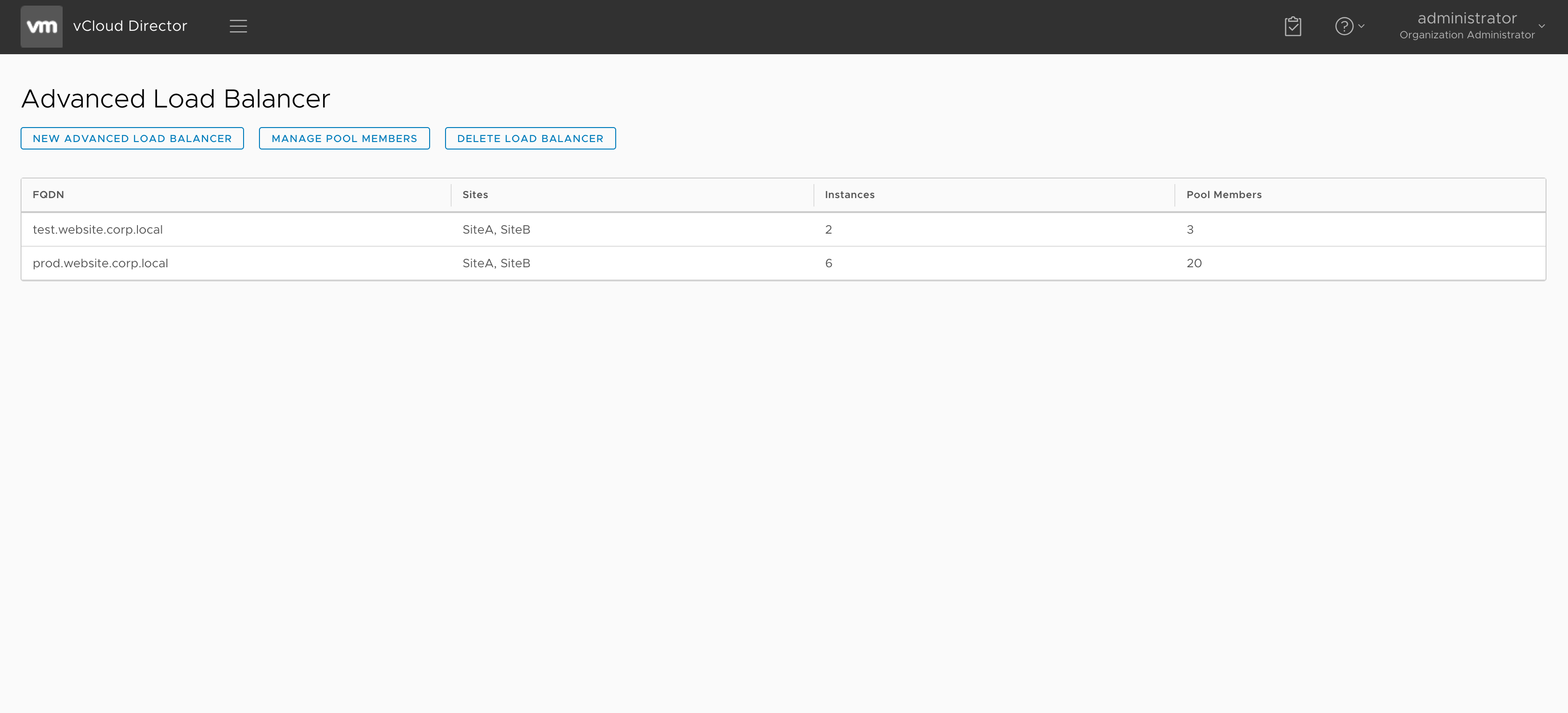
Create a New Advanced Load Balancer
From an end-user perspective, creating an advanced load balancer is relatively simple – you just fill in a form provided by the Advanced Load Balancing UI extension.
In the form, you provide:
- FQDN of the load balancer
- Number of instances per site
- Pool members on both sites
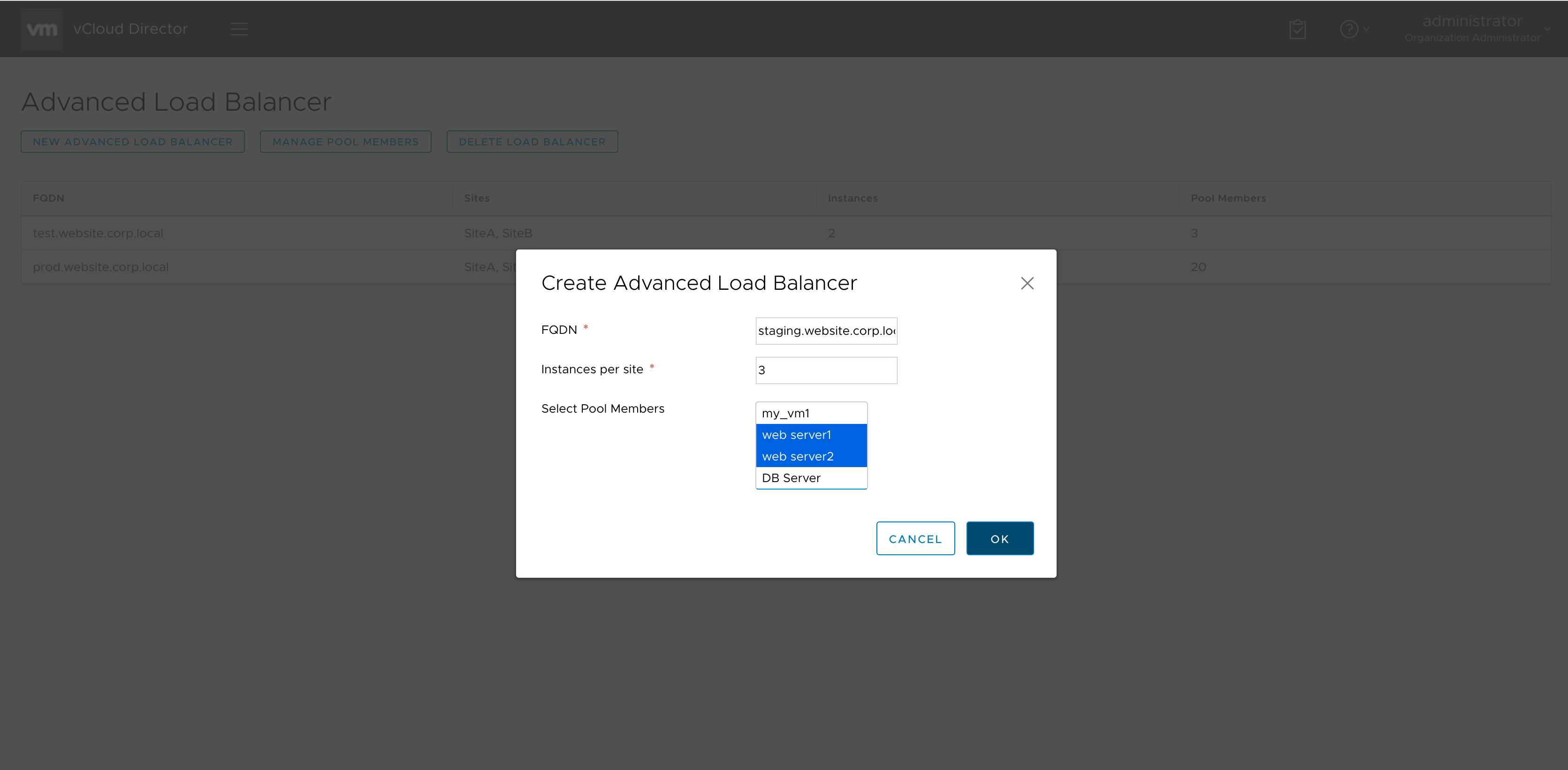
In the backend, the workflow determines where to create the NSX load balancers based on the site where the VMs reside.
NSX Load Balancer Configuration
After the advanced load balancer is created, it will deploy identical NSX load balancers on each site to allow scaling across sites. This also depends on the edge gateways to which the virtual machines are connected.
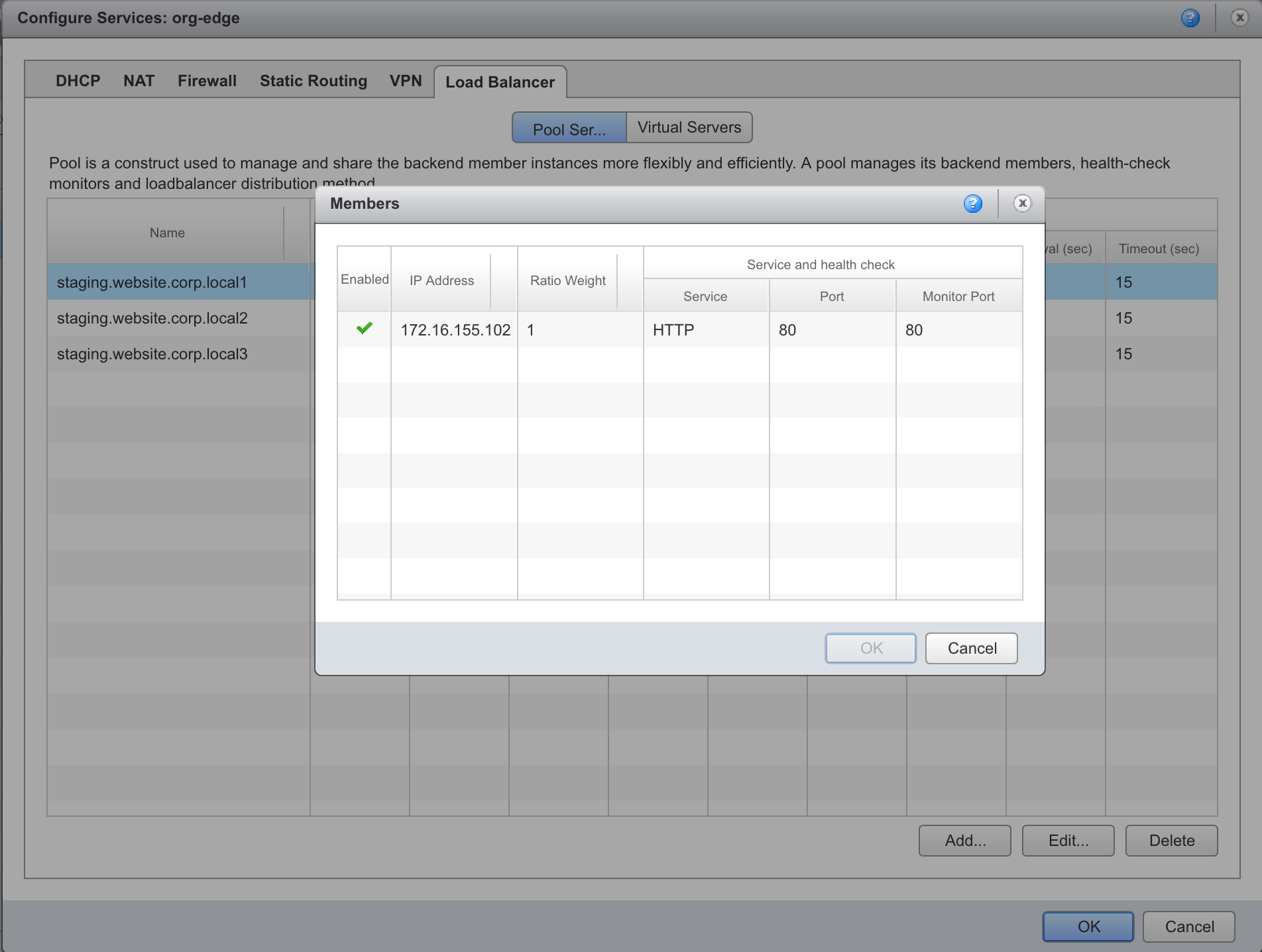
F5 Configuration
When all the NSX load balancers are ready, the workflow will create all the needed F5 objects to allow DNS based load balancing.
The Wide IP is the FQDN of the advanced load balancer.
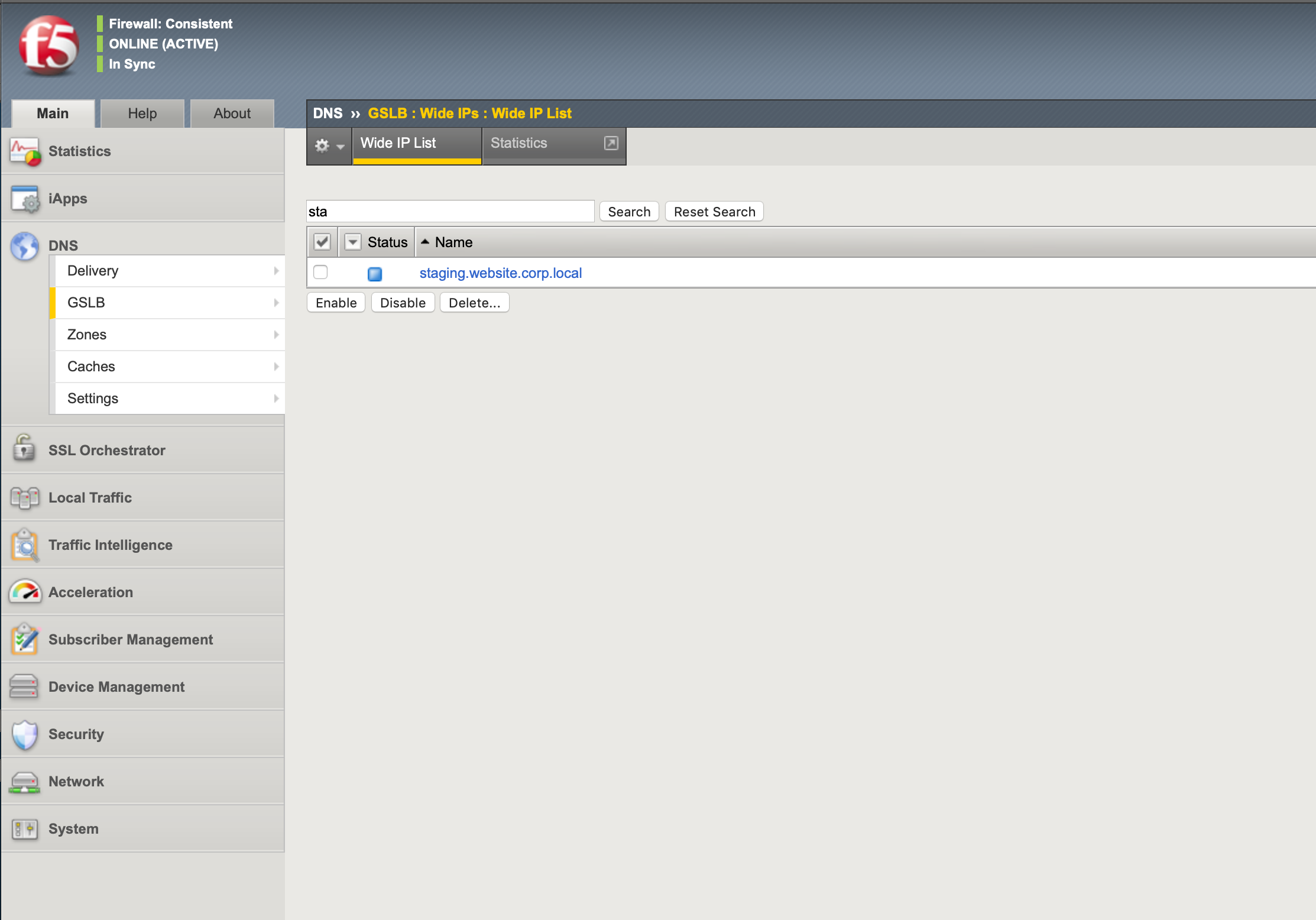
It also defines how requests are going to be balanced across the Wide IP pool members.
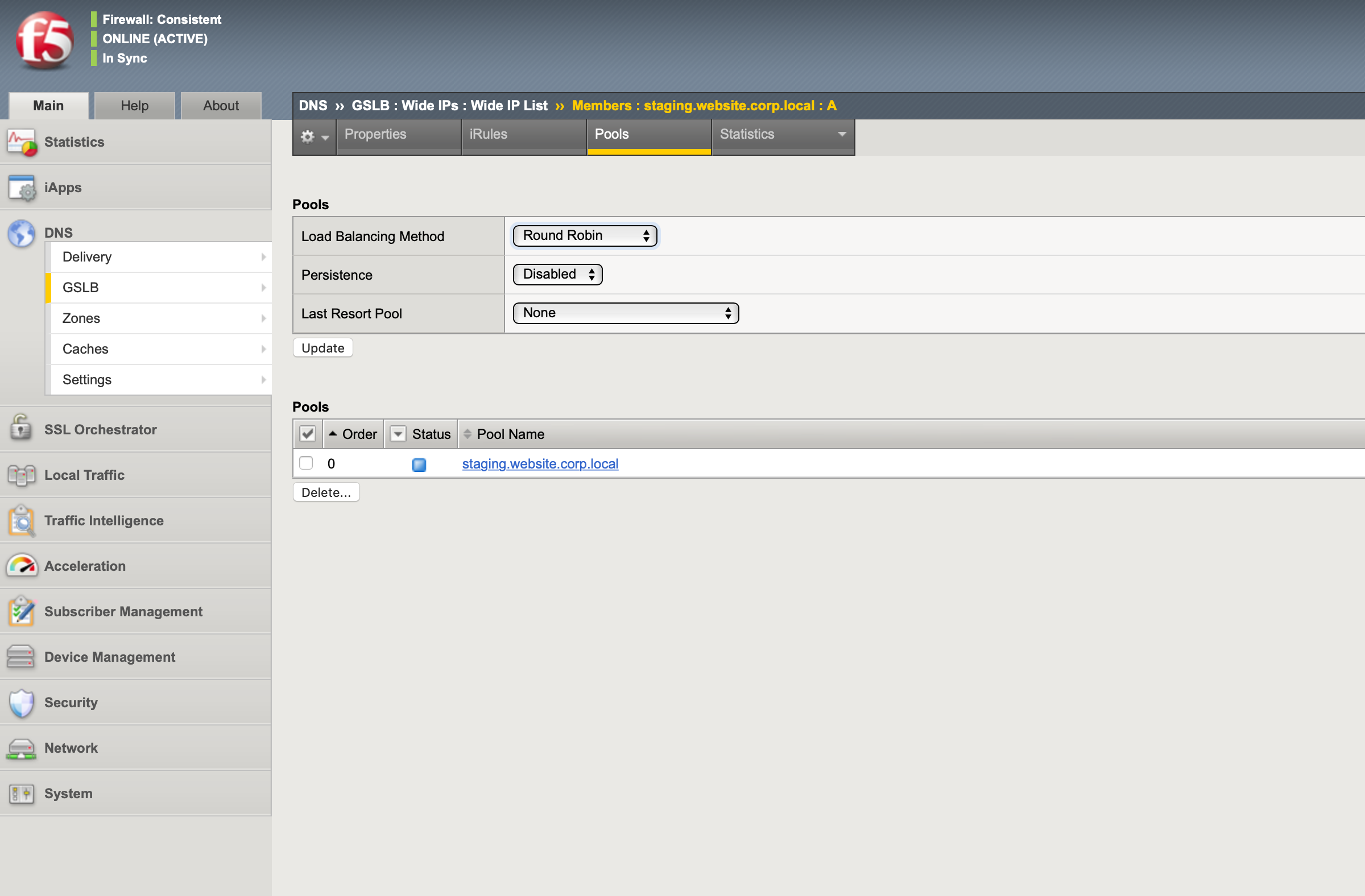
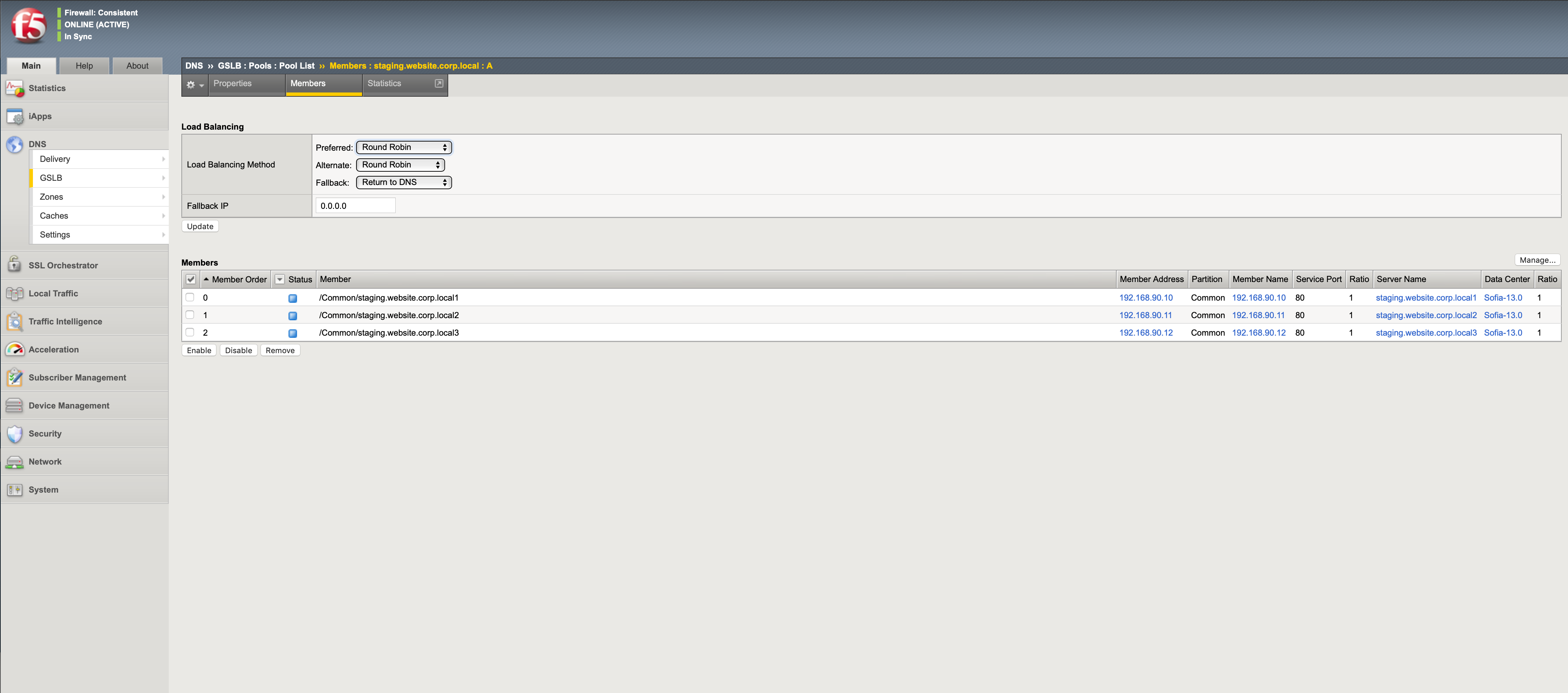
The pool members are the virtual server VIP addresses of the load balancers created in NSX.
Conclusion
F5 Big-IP integration with vCloud Director allows tenants to easily create complex load balancing solutions required to support global scalable applications. In this blog post, we have discussed the basic setup. However, DNS-based load balancing usually requires a lot of configuration, which can either be exposed to tenants, or kept as a provider side configuration in the solution, thus hiding the complexity from the end-user. Most importantly, everything is managed through the vCloud Director Portal, giving a unified experience to the end-users.
For more information on vCloud Director, please visit https://www.vmware.com/products/vcloud-director.html