By following this guide, you will be able to successfully self-host your preferred DeepSeek model on a home lab or home office server, harnessing the potential of these AI models in a private and controlled environment.
DeepSeek is a powerful AI model that can be self-hosted locally for faster performance, improved privacy, and flexible configuration. This guide demonstrates how to self-host DeepSeek in a home lab environment, allowing access from multiple devices on your local network. We will cover self-hosting DeepSeek, configuring a web interface and running it as an always online service.
Self-hosted DeepSeek accessed via wired LAN devices and also non-guest Wi-Fi network.
In This Article
Why Self Host DeepSeek
Contents
Note: DeepSeek-R1 is a 671B model with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture requiring 1.5 TB of VRAM, making it impractical for consumer hardware. DeepSeek-R1 distilled models, like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-LLaMA-70B, are fine-tuned versions of open-source models like LLaMA and Qwen, trained on data generated by DeepSeek-R1. Thus, inheriting DeepSeek’s reasoning capabilities while being far more efficient to self-host. Enjoy!
Self-hosting DeepSeek gives you:
- Privacy: Data is on your infrastructure, not 3rd party servers.
- Speed: Low network latency. Especially if you will be running the smaller models.
- Custom Hardware: Config CPU, GPU, and memory allocation to your needs.
- Scalability: Expand your home lab as needed.
- Control: No external dependencies or vendor lock-in.
- Learning: Enhance your skills by managing and optimizing your own AI infrastructure.
Why not
A few of the challenges are:
- Model Bias and Censorship: Restricted/censored responses on sensitive topics (or use open-r1).
- Cost: High initial and ongoing expenses for hardware and electricity.
- Longevity: Future AI models will likely require fairly frequent hardware upgrades.
- Maintenance: Requires regular updates and ongoing technical upkeep.
- Scalability Limits: Physical space, noise, and heat challenges can hinder expansion.
Preparing to Self-Host DeepSeek
Before setting up DeepSeek, ensure your system meets the necessary hardware requirements, especially if running larger models that require high RAM and GPU resources.
- CPU: Powerful multi-core processor (12+ cores recommended) for handling multiple requests.
- GPU: NVIDIA GPU with CUDA support for accelerated performance. AMD will also work. (less popular/tested)
- RAM: Minimum 16 GB, preferably 32 GB or more for larger models.
- Storage: NVMe storage for faster read/write operations.
- Operating System: Ubuntu or Ubuntu-based distributions are preferred for compatibility.
- Censorship/restrictions: If you are looking for DeepSeek-R1 with no censorship or content restrictions, try open-r1.
- Distilled models: Read more about these official models here: api-docs.deepseek.com/news/news250120.
- More detailed hardware guidance can be found here.
Here are three recommended GPUs: NVIDIA RTX 4080, NVIDIA RTX 4090, and the NVIDIA A100. Find them also on eBay used.
Install
Please read the Installing DeepSeek on Linux in 3 mins guide for detailed steps.
In short, install and run using:
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh ollama run deepseek-r1:8b
Run DeepSeek with a Web Interface (Open WebUI)
By leveraging Open WebUI, you can effortlessly interact with DeepSeek through a centralized, user-friendly dashboard accessible from any device on your local network. Open WebUI can be installed using pip, the Python package installer.
Install Open WebUI:
Open your terminal and run the following command to install Open WebUI:
pip install open-webui
Alternatively, you can install with Snap instead:
sudo apt update sudo apt install snapd sudo snap install open-webui --beta
Running Open WebUI:
After installation, you can start Open WebUI by executing:
open-webui serve
This will start the Open WebUI server, which you can access at http://localhost:8080 or replace `localhost` with your server’s local IP address to access from other devices on your network. More on that later!
Using SSH Tunnel (Recommended)
Screenshot of Open WebUI showing chat interaction with DeepSeek R1
SSH tunneling can be used to securely connect your PC to the DeepSeek server within your home network. This ensures that the connection is encrypted and only accessible from your LAN (Local Area Network) devices.
How this works:
- SSH Connection: Uses SSH (usually on port 22) to create an encrypted tunnel.
- Port Forwarding: Forwards a port from your local machine to your server on the same LAN, allowing secure access to Open WebUI.
Steps to Set Up SSH Tunneling:
- Ensure SSH Server is Installed on the Local Server:
sudo apt update sudo apt install openssh-server
- Start and Enable the SSH Service on the Local Server:
sudo systemctl start ssh sudo systemctl enable ssh
Note: On some distributions, the service might be named
sshdinstead ofssh. Verify the service name using:sudo systemctl status ssh # or sudo systemctl status sshd
- Configure the Firewall on the Local Server to Allow SSH and Open WebUI Ports:Note: Replace
ufwwith your firewall manager if different.Allow SSH (Port 22) from Local Network:sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port 22 proto tcp
Replace
192.168.1.0/24with your local network’s subnet if different.Allow Open WebUI (Port 8080) from Local Network:
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.1.0/24 to any port 8080 proto tcp
Replace
192.168.1.0/24with your local network’s subnet if different. - SSH Tunnel from Your Local Machine: On your local machine, run:
ssh -L 8080:localhost:8080 user@192.168.1.100
Replace
8080with your preferred port,userwith your SSH username, and192.168.1.100with the DeepSeek server’s local IP address.Explanation:
-L 8080:localhost:8080user@192.168.1.100: Replaceuserwith your SSH username and192.168.1.100with the server’s local IP address. - (Optional) If SSH is on a different port (e.g., 2222), use the
-pflag:ssh -p 2222 -L 8080:localhost:8080 user@192.168.1.100
- Access Open WebUI Locally: Once the SSH tunnel is established, open your browser and go to:
http://localhost:8080
Now, Open WebUI is only accessible on your local home/office network via
http://localhost:8080.
Advantages:
- Security: Traffic is encrypted via SSH tunnel.
- No extra ports open: Including the SSH port, which is only accessible from within your local network
- Easy: Uses existing SSH infrastructure. It’s likely you would have SSH already enabled on a home or office server.
Considerations:
- Manual: Requires a tunnel to be established each time you want to access Open WebUI.
- Local Port Available: Make sure your local port 8080 is free, or choose a different local port.
- Persistent Tunnels: For automatic reconnection, consider using tools like
autossh.
Automation: While the manual method requires setting up the tunnel each time, you can automate this process using tools like autossh to maintain persistent tunnels that also automatically reconnects:
sudo apt install autossh autossh -M 0 -f -N -L 8080:localhost:8080 user@192.168.1.100
Using Reverse Proxy with Nginx
You can also consider instead, placing DeepSeek behind Nginx:
-
- Install Nginx:
sudo apt install nginx
- Create a Reverse Proxy Config:
sudo vi /etc/nginx/sites-available/deepseek
- Add the following configuration:
server { listen 80; server_name your-local-domain.local; location / { proxy_pass http://localhost:8080; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; } } - Enable and Restart Nginx:
sudo ln -s /etc/nginx/sites-available/deepseek /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/ sudo nginx -t # Test the configuration sudo systemctl restart nginx
- Install Nginx:
Now, access via: https://your-local-domain.local/
Conclusion
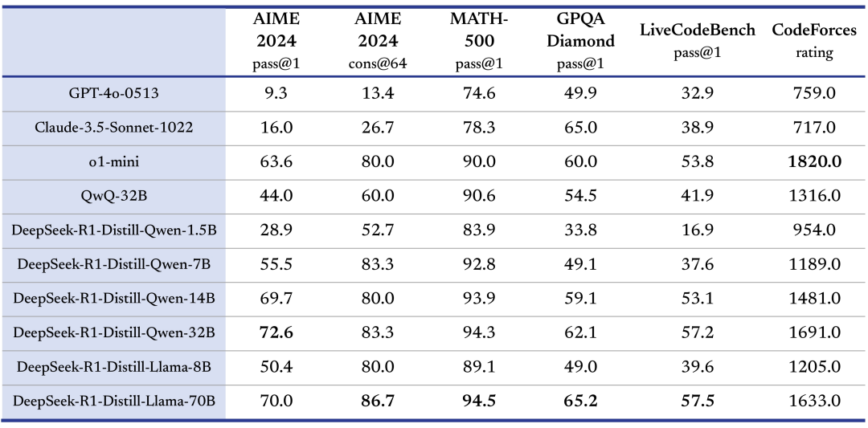
Benchmark table: 6 models Distilled from DeepSeek-R1 and fully open-sourced
Running DeepSeek in your home lab offers more control, privacy, and performance. Self-hosting DeepSeek also eliminates reliance on external cloud dependencies, increases security, and offers more customization options. Perfect for home lab enthusiasts, developers, and professionals.
* DeepSeek-R1 is a 671B model with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) architecture that allows for task specialization. It requires around 1.5 TB of VRAM, making installing it far beyond the self-host capabilities of consumer hardware. It was trained from scratch on a diverse dataset to achieve strong reasoning and language understanding. DeepSeek-R1-Distill models are fine-tuned versions of open-source models like LLaMA and Qwen trained on data generated by DeepSeek-R1. These distilled models like DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-LLaMA-70B inherit the base models of their respective models but get the reasoning capabilities introduced by DeepSeek’s fine-tuning. They are more efficient and practical to deploy on consumer hardware compared to the full DeepSeek-R1 model, which requires a ton of compute resources. Enjoy!
Update: May 1st, 2025:
Quantization for Optimizing Performance
Quantization is a technique that really opens up the possibilities for running DeepSeek models on a wider range of hardware. By lowering the precision of model weights and activations, you can greatly reduce memory usage and processing requirements while still maintaining accuracy.
That’s where quantization comes in. By transforming model weights and activations into 4-bit values, you can reduce the model size by nearly 8:1 compared to standard 32-bit. Of course, aggressive compression can introduce some accuracy loss due to quantization bias. So it’s best suited for scenarios where resource efficiency really is your top priority!
8-bit quantization strikes a balance between efficiency and accuracy. By capping precision at 8 bits, you reduce model memory requirements to a quarter of what they are with 32-bit floating point. That also gives you a significant boost in computational throughput. And, crucially, INT8 quantization usually preserves model accuracy well. That makes it a popular choice for real-time applications like conversational AI, image processing and chatbots.
FP32 precision remains the gold standard for model training and any scenario where maximum accuracy is essential. That comes at a cost, though: much greater memory consumption and slower inference speeds. You typically need powerful GPUs or TPUs for that. So it’s generally reserved for research, model development or specialized tasks where even minor accuracy losses just aren’t acceptable.
One recent advancement that’s helped with this is dynamic quantization. That allows you to quantize different layers or components of the DeepSeek model at varying bit-widths based on their importance. So critical layers like attention mechanisms might use 4 or 6 bits, while less sensitive layers can be quantized as low as 1.58 bits. This technique has enabled reductions in model size of up to 80%, making it feasible to run large DeepSeek models on systems with as little as 20 GB of RAM, though with slower processing speeds.
Dynamic quantization offers advanced users the flexibility to fine-tune that balance between size and performance. However, you should test your models for accuracy.
References:
— Fine-Tuning DeepSeek v3 & R1 to optimize quality, latency, & cost
— Dynamic quantization model that reduces the size of DeepSeek-R1 by up to 80%