ADVERTISEMENT

Nagios is a free, open-source monitoring tool which helps us to monitor services and applications that run on Windows, Linux, Routers, and other network devices.
With the help of Nagios graphical interface, you can monitor basic services (FTP, HTTP, SSH, etc..) and attributes (system load, memory, CPU usage, etc.).
In this post, we will see how to install Nagios on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 and how to monitor application services with Nagios plugins.
THIS DOCUMENT IS ALSO AVAILABLE FOR
Prerequisites
Contents
Nagios requires Web Server (httpd), PHP, compilers and development libraries.
Install all packages in a single command.
yum -y install httpd php gcc glibc glibc-common wget perl gd gd-devel unzip zip tar
Create a user and group for allowing the external commands to be executed through the web interface. Add the user and apache user to be a part of the created group.
useradd nagios groupadd nagcmd usermod -a -G nagcmd nagios usermod -a -G nagcmd apache
Install Nagios
Download the Nagios Core from the official site using the terminal.
cd /tmp/ wget https://assets.nagios.com/downloads/nagioscore/releases/nagios-4.4.5.tar.gz tar -zxvf nagios-4.4.5.tar.gz cd /tmp/nagios-4.4.5/
Compile and install Nagios core on your system.
./configure --with-nagios-group=nagios --with-command-group=nagcmd make all make install make install-init make install-config make install-commandmode
Install Nagios Web Interface
Install the Nagios web interface using the following command.
make install-webconf
Create a user account (nagiosadmin) for the Nagios web interface. Remember the password that you set for this user – you will need it later.
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
Restart Apache web server.
systemctl restart httpd systemctl enable httpd
Configure Nagios
Nagios places configuration files under the /usr/local/nagios/etc directory. The default configurations should work just fine for Nagios.
We will make just one change before we proceed.
Edit the /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg config file and change the email address associated with the nagiosadmin contact definition to your email address to receive alerts.
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
Replace the email address field to receive the notification.
ADVERTISEMENT
define contact { contact_name nagiosadmin ; Short name of user use generic-contact ; Inherit default values from generic-contact template (defined above) alias Nagios Admin ; Full name of user email admin@itzgeek.com ; <<***** CHANGE THIS TO YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS ******
}
Install Nagios Plugins
Download Nagios Plugins to /tmp directory and extract it.
cd /tmp wget https://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.2.1.tar.gz tar -zxvf nagios-plugins-2.2.1.tar.gz cd /tmp/nagios-plugins-2.2.1/
Compile and install the Nagios plugins.
./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios make make install
Start Nagios
Verify the sample Nagios configuration files.
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
Output:
Nagios Core 4.4.5 Copyright (c) 2009-present Nagios Core Development Team and Community Contributors Copyright (c) 1999-2009 Ethan Galstad Last Modified: 2019-08-20 License: GPL Website: https://www.nagios.org Reading configuration data... Read main config file okay... Read object config files okay... Running pre-flight check on configuration data... Checking objects... Checked 8 services. Checked 1 hosts. Checked 1 host groups. Checked 0 service groups. Checked 1 contacts. Checked 1 contact groups. Checked 24 commands. Checked 5 time periods. Checked 0 host escalations. Checked 0 service escalations. Checking for circular paths... Checked 1 hosts Checked 0 service dependencies Checked 0 host dependencies Checked 5 timeperiods Checking global event handlers... Checking obsessive compulsive processor commands... Checking misc settings... Total Warnings: 0 Total Errors: 0 Things look okay - No serious problems were detected during the pre-flight check
If there are no errors, start the Nagios service.
systemctl start nagios
Enable Nagios on system startup.
systemctl enable nagios
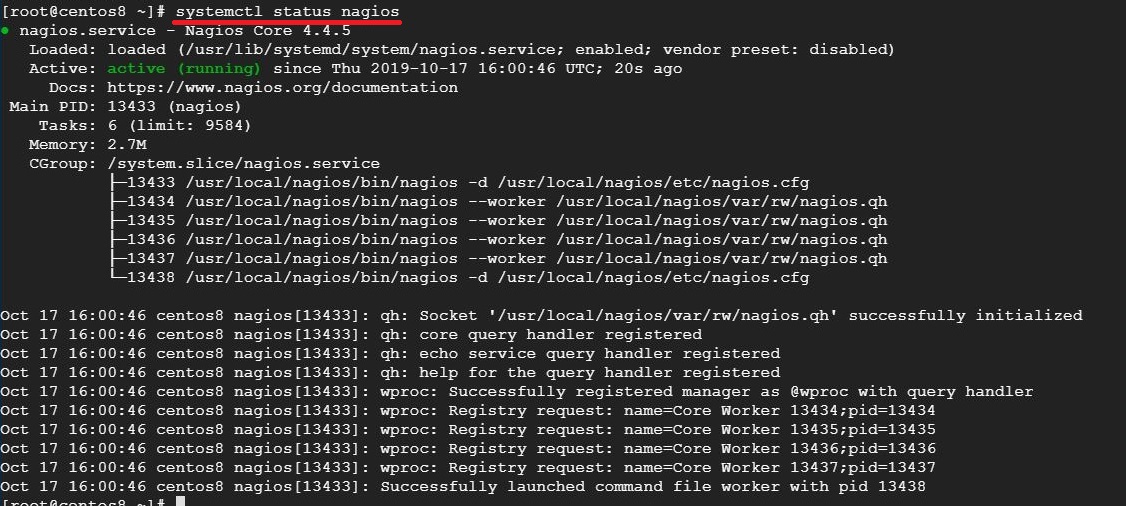
Check Nagios service status with the below command.
systemctl status nagios
SELinux
See if SELinux is in Enforcing mode.
getenforce
Change SELinux mode to Permissive or disable.
setenforce 0
To make this SELinux mode permanent, modify /etc/selinux/config and reboot the system.
Firewall
Create a firewall rule to allow webserver access through the firewall.
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http firewall-cmd --reload
Access Nagios Web Interface
Access the Nagios web interface using the below URL.
http://ip-add-re-ss/nagios/
You will need to use the username (nagiosadmin) and password you specified earlier to access Nagios web interface.
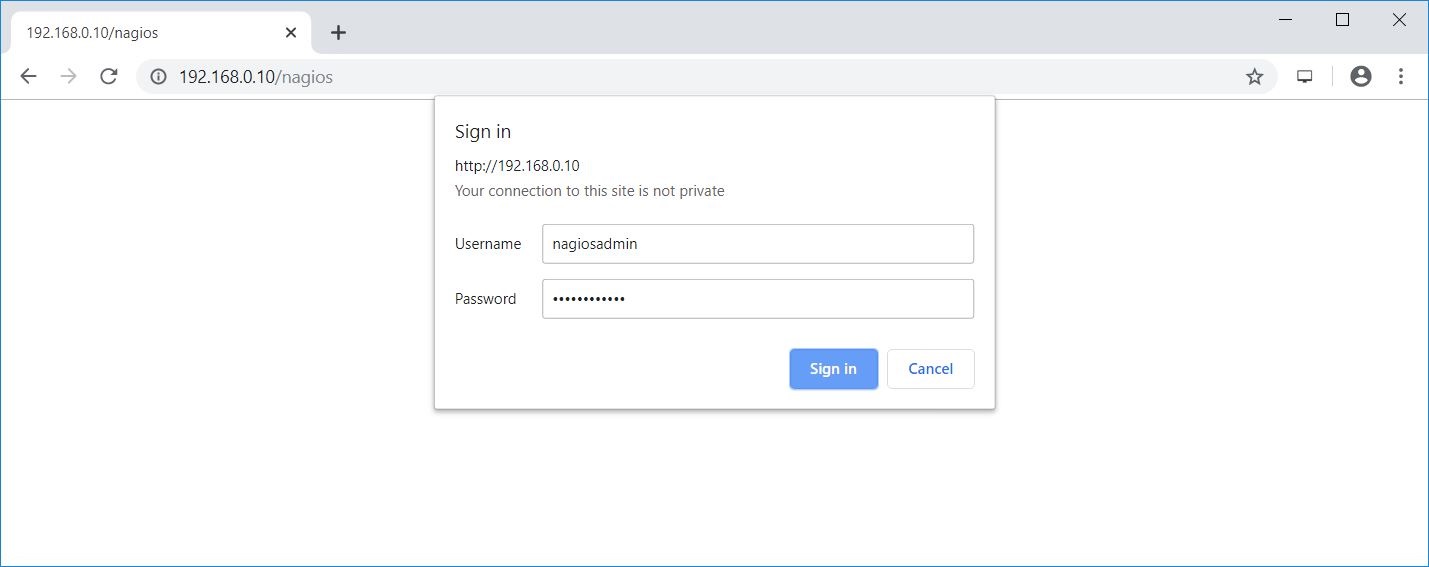
Nagios console will look like below.
After you logged in to Nagios web interface, click on Hosts in the left pane to see a list of systems being monitored by Nagios.
ADVERTISEMENT
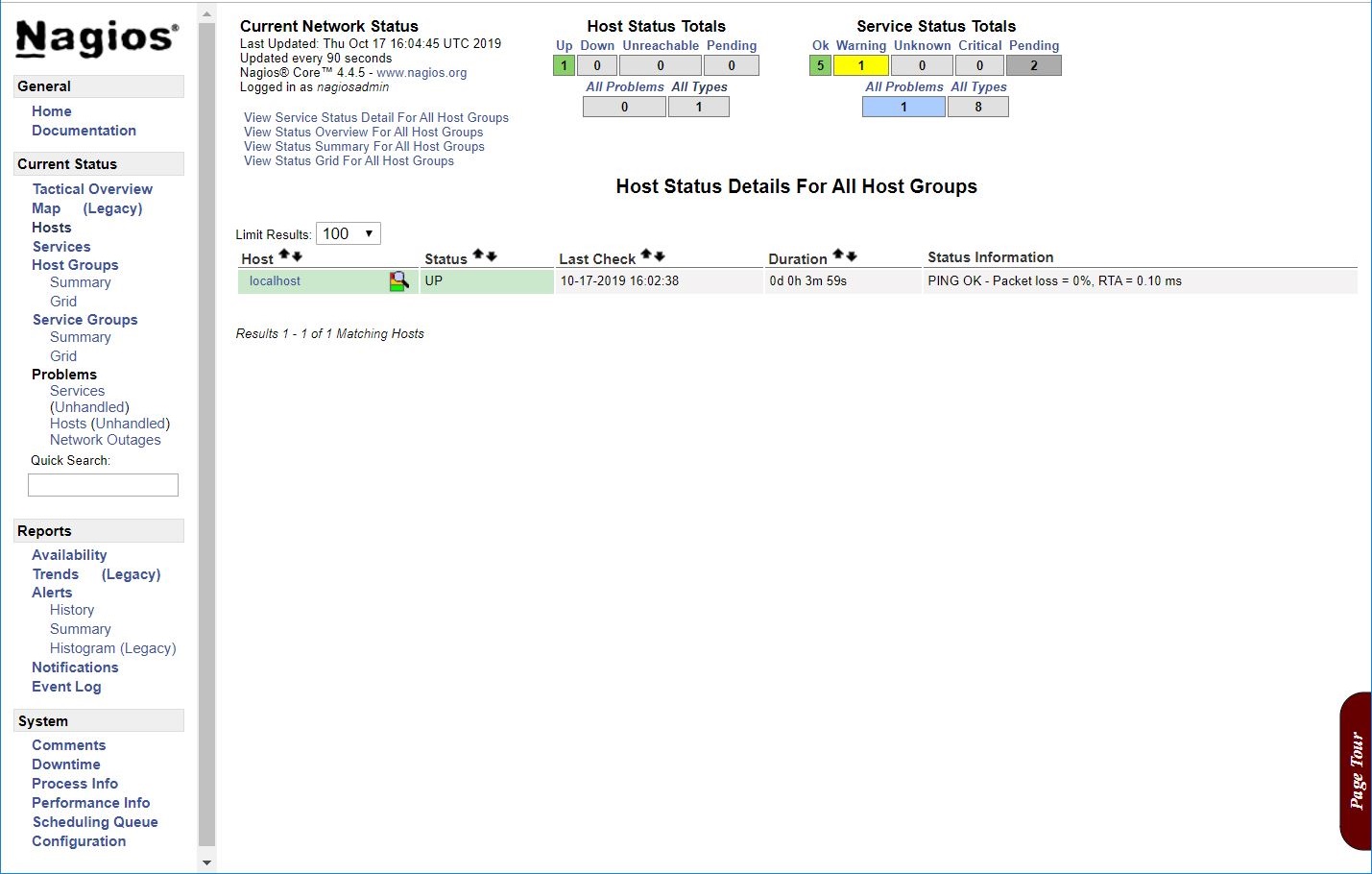
Since we have not added any host to Nagios, it just monitors the localhost itself.
Click on Services in the left pane to check the status of any services that are being monitored with Nagios.
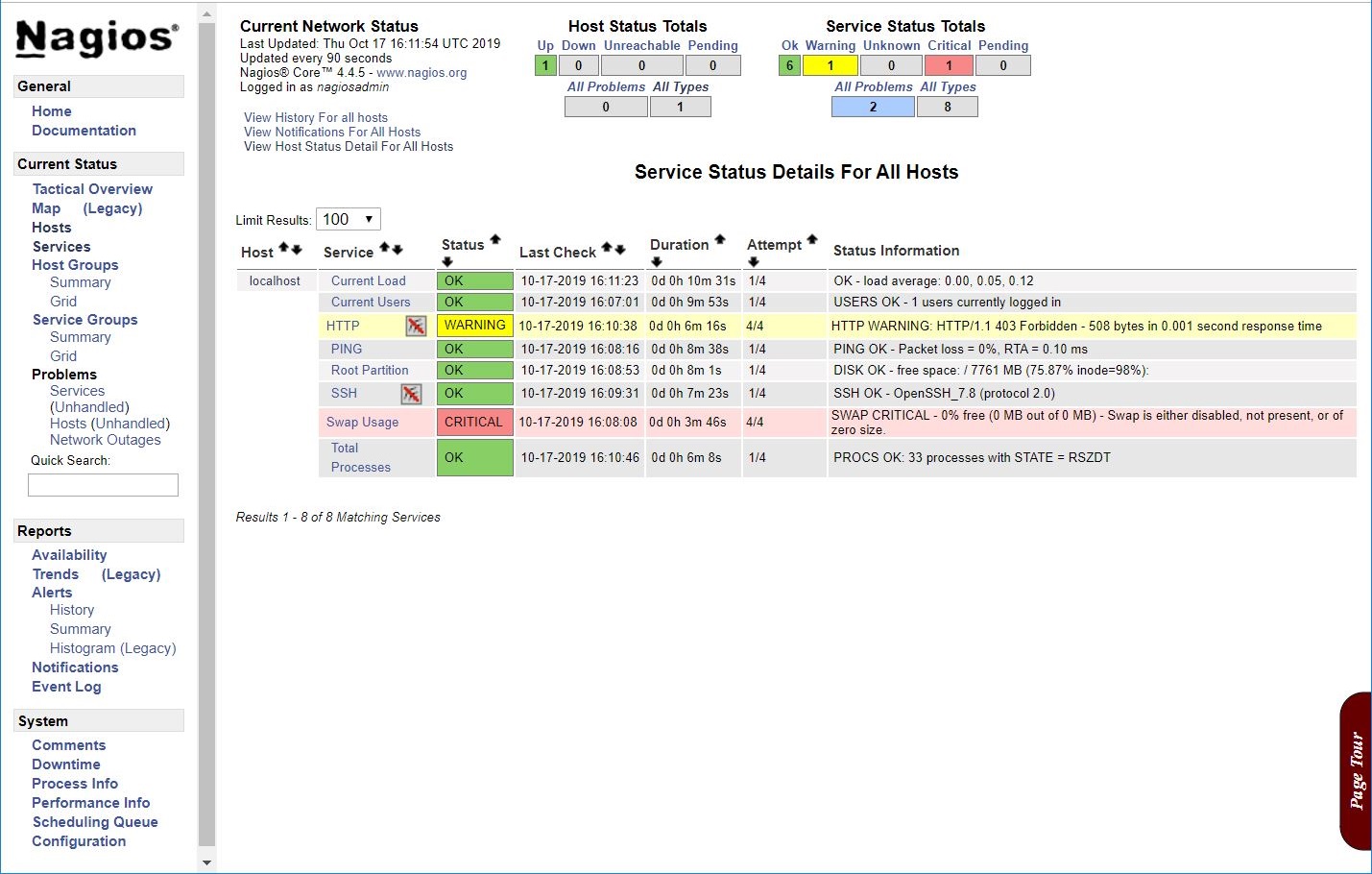
Conclusion
In this post, you have learned how to install Nagios on CentOS 8 / RHEL 8 and configured Nagios to monitor the services with the help of Nagios plugins. At this moment, Nagios monitors the server itself. You can also monitor the Remote Linux System with Nagios with NRPE add-on.